Bispectrum-based Cross-frequency Functional Connectivity: Classification of Alzheimer's disease
Paper and Code
Jun 10, 2022
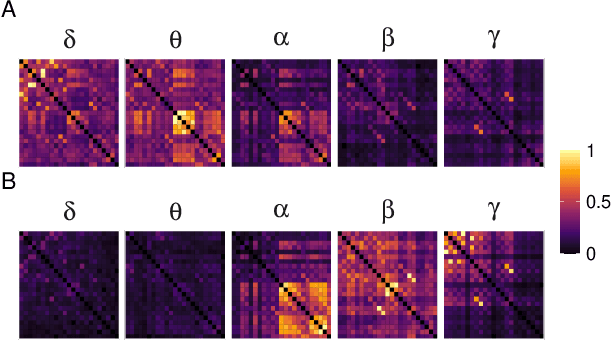
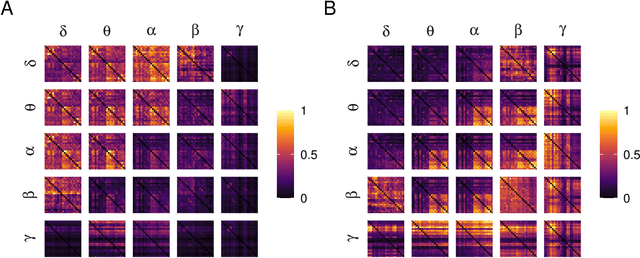
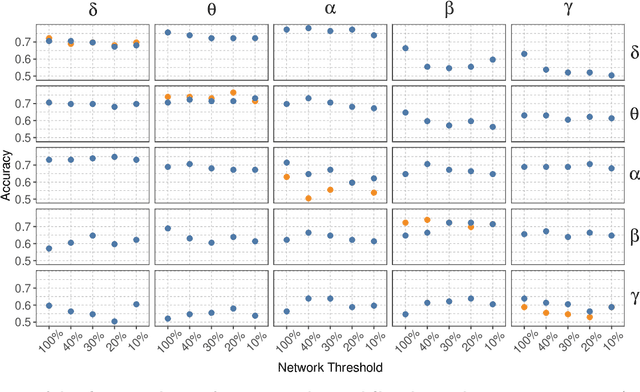
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease known to affect brain functional connectivity (FC). Linear FC measures have been applied to study the differences in AD by splitting neurophysiological signals such as electroencephalography (EEG) recordings into discrete frequency bands and analysing them in isolation. We address this limitation by quantifying cross-frequency FC in addition to the traditional within-band approach. Cross-bispectrum, a higher-order spectral analysis, is used to measure the nonlinear FC and is compared with the cross-spectrum, which only measures the linear FC within bands. Each frequency coupling is then used to construct an FC network, which is in turn vectorised and used to train a classifier. We show that fusing features from networks improves classification accuracy. Although both within-frequency and cross-frequency networks can be used to predict AD with high accuracy, our results show that bispectrum-based FC outperforms cross-spectrum suggesting an important role of cross-frequency FC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge