Beyond Transduction: A Survey on Inductive, Few Shot, and Zero Shot Link Prediction in Knowledge Graphs
Paper and Code
Dec 08, 2023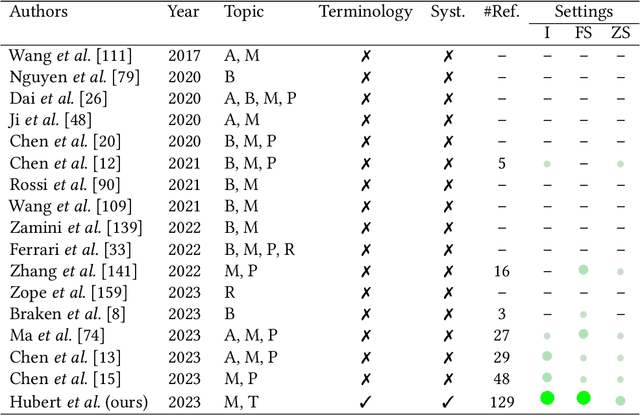
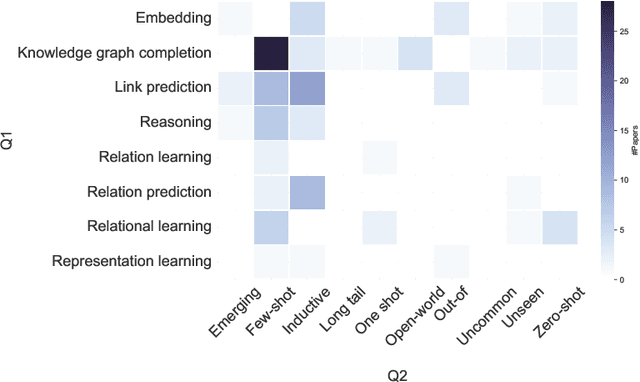

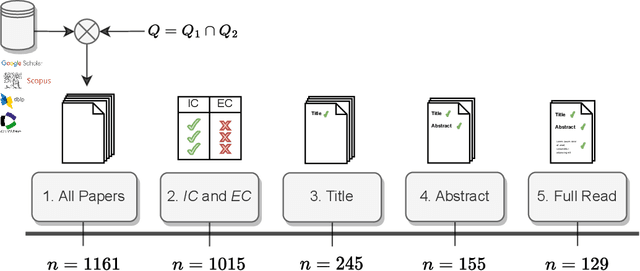
Knowledge graphs (KGs) comprise entities interconnected by relations of different semantic meanings. KGs are being used in a wide range of applications. However, they inherently suffer from incompleteness, i.e. entities or facts about entities are missing. Consequently, a larger body of works focuses on the completion of missing information in KGs, which is commonly referred to as link prediction (LP). This task has traditionally and extensively been studied in the transductive setting, where all entities and relations in the testing set are observed during training. Recently, several works have tackled the LP task under more challenging settings, where entities and relations in the test set may be unobserved during training, or appear in only a few facts. These works are known as inductive, few-shot, and zero-shot link prediction. In this work, we conduct a systematic review of existing works in this area. A thorough analysis leads us to point out the undesirable existence of diverging terminologies and task definitions for the aforementioned settings, which further limits the possibility of comparison between recent works. We consequently aim at dissecting each setting thoroughly, attempting to reveal its intrinsic characteristics. A unifying nomenclature is ultimately proposed to refer to each of them in a simple and consistent manner.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge