Best Viewpoints for External Robots or Sensors Assisting Other Robots
Paper and Code
Jul 20, 2020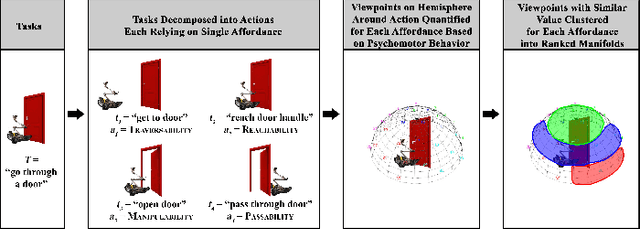
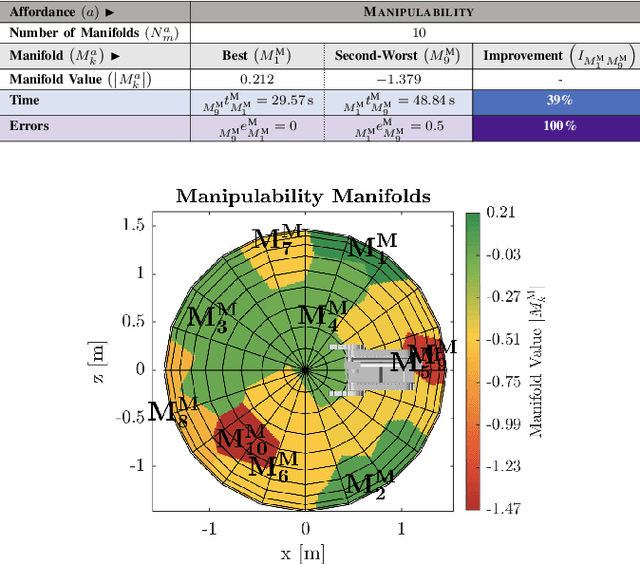
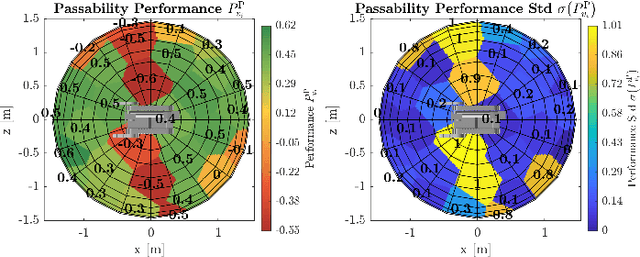
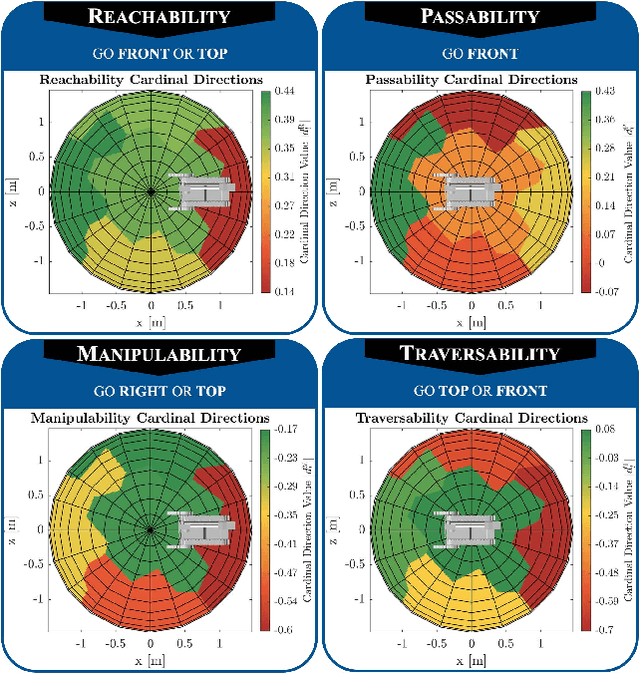
This work creates a model of the value of different external viewpoints of a robot performing tasks. The current state of the practice is to use a teleoperated assistant robot to provide a view of a task being performed by a primary robot; however, the choice of viewpoints is ad hoc and does not always lead to improved performance. This research applies a psychomotor approach to develop a model of the relative quality of external viewpoints using Gibsonian affordances. In this approach, viewpoints for the affordances are rated based on the psychomotor behavior of human operators and clustered into manifolds of viewpoints with the equivalent value. The value of 30 viewpoints is quantified in a study with 31 expert robot operators for 4 affordances (Reachability, Passability, Manipulability, and Traversability) using a computer-based simulator of two robots. The adjacent viewpoints with similar values are clustered into ranked manifolds using agglomerative hierarchical clustering. The results show the validity of the affordance-based approach by confirming that there are manifolds of statistically significantly different viewpoint values, viewpoint values are statistically significantly dependent on the affordances, and viewpoint values are independent of a robot. Furthermore, the best manifold for each affordance provides a statistically significant improvement with a large Cohen's d effect size (1.1-2.3) in performance (improving time by 14%-59% and reducing errors by 87%-100%) and improvement in performance variation over the worst manifold. This model will enable autonomous selection of the best possible viewpoint and path planning for the assistant robot.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge