BERT-based Ranking for Biomedical Entity Normalization
Paper and Code
Aug 09, 2019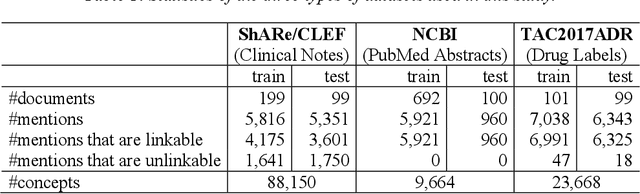

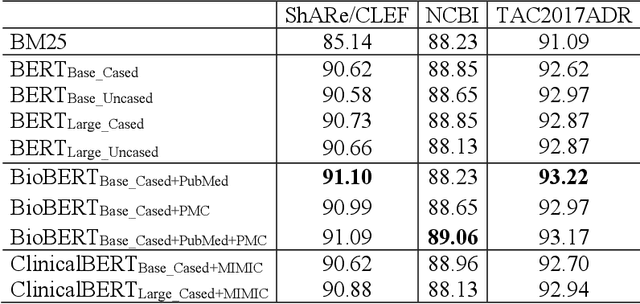
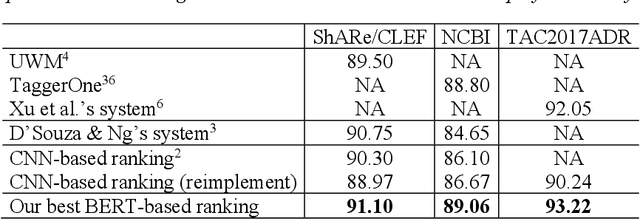
Developing high-performance entity normalization algorithms that can alleviate the term variation problem is of great interest to the biomedical community. Although deep learning-based methods have been successfully applied to biomedical entity normalization, they often depend on traditional context-independent word embeddings. Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT), BERT for Biomedical Text Mining (BioBERT) and BERT for Clinical Text Mining (ClinicalBERT) were recently introduced to pre-train contextualized word representation models using bidirectional Transformers, advancing the state-of-the-art for many natural language processing tasks. In this study, we proposed an entity normalization architecture by fine-tuning the pre-trained BERT / BioBERT / ClinicalBERT models and conducted extensive experiments to evaluate the effectiveness of the pre-trained models for biomedical entity normalization using three different types of datasets. Our experimental results show that the best fine-tuned models consistently outperformed previous methods and advanced the state-of-the-art for biomedical entity normalization, with up to 1.17% increase in accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge