Behavior-based Navigation of Mobile Robot in Unknown Environments Using Fuzzy Logic and Multi-Objective Optimization
Paper and Code
Mar 09, 2017


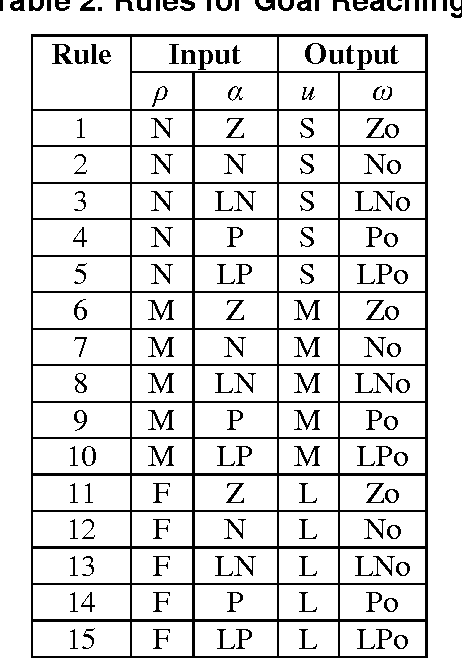
This study proposes behavior-based navigation architecture, named BBFM, to deal with the problem of navigating the mobile robot in unknown environments in the presence of obstacles and local minimum regions. In the architecture, the complex navigation task is split into principal sub-tasks or behaviors. Each behavior is implemented by a fuzzy controller and executed independently to deal with a specific problem of navigation. The fuzzy controller is modified to contain only the fuzzification and inference procedures so that its output is a membership function representing the behavior's objective. The membership functions of all controllers are then used as the objective functions for a multi-objective optimization process to coordinate all behaviors. The result of this process is an overall control signal, which is Pareto-optimal, used to control the robot. A number of simulations, comparisons, and experiments were conducted. The results show that the proposed architecture outperforms some popular behavior-based architectures in term of accuracy, smoothness, traveled distance, and time response.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge