Batch-based Activity Recognition from Egocentric Photo-Streams Revisited
Paper and Code
May 09, 2018
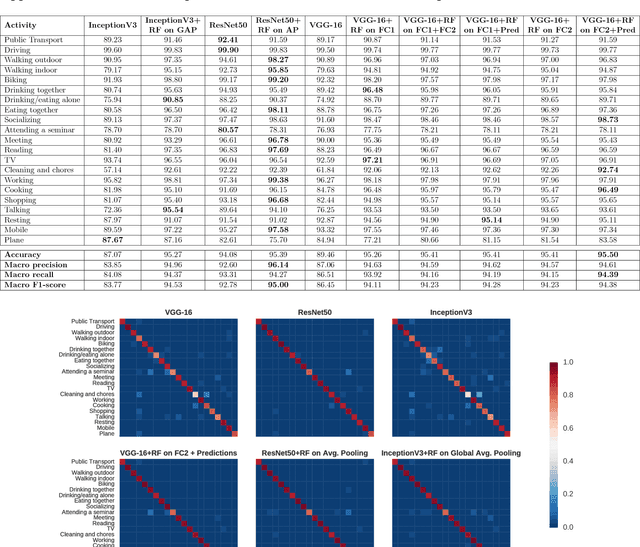
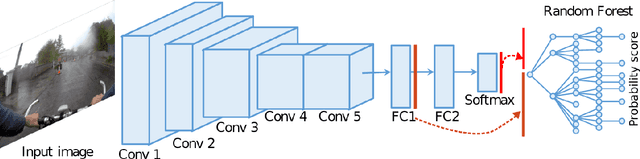
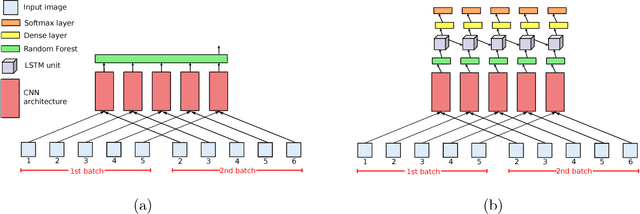
Wearable cameras can gather large a\-mounts of image data that provide rich visual information about the daily activities of the wearer. Motivated by the large number of health applications that could be enabled by the automatic recognition of daily activities, such as lifestyle characterization for habit improvement, context-aware personal assistance and tele-rehabilitation services, we propose a system to classify 21 daily activities from photo-streams acquired by a wearable photo-camera. Our approach combines the advantages of a Late Fusion Ensemble strategy relying on convolutional neural networks at image level with the ability of recurrent neural networks to account for the temporal evolution of high level features in photo-streams without relying on event boundaries. The proposed batch-based approach achieved an overall accuracy of 89.85\%, outperforming state of the art end-to-end methodologies. These results were achieved on a dataset consists of 44,902 egocentric pictures from three persons captured during 26 days in average.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge