Balancing the composition of word embeddings across heterogenous data sets
Paper and Code
Jan 14, 2020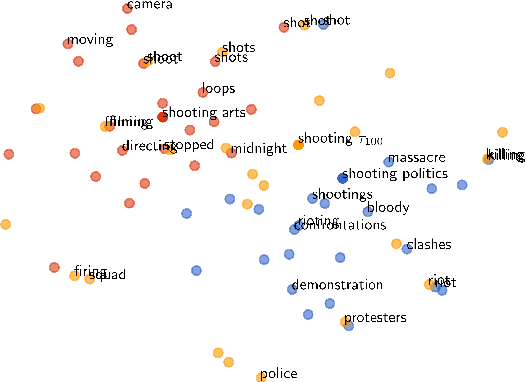
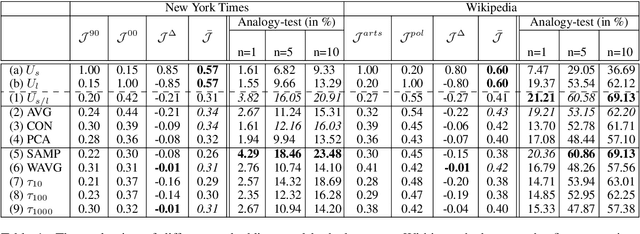
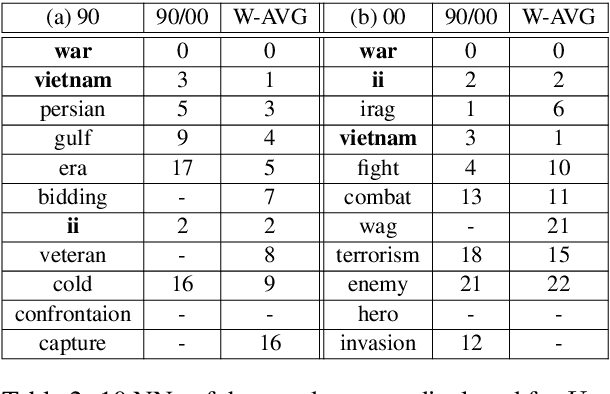
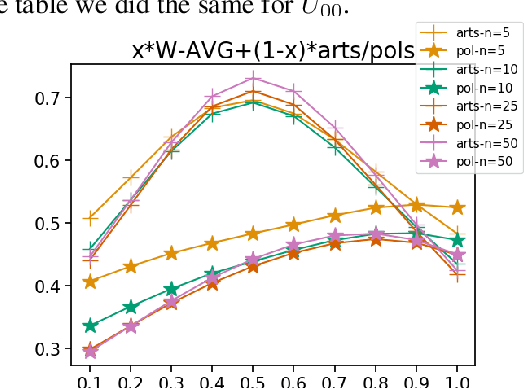
Word embeddings capture semantic relationships based on contextual information and are the basis for a wide variety of natural language processing applications. Notably these relationships are solely learned from the data and subsequently the data composition impacts the semantic of embeddings which arguably can lead to biased word vectors. Given qualitatively different data subsets, we aim to align the influence of single subsets on the resulting word vectors, while retaining their quality. In this regard we propose a criteria to measure the shift towards a single data subset and develop approaches to meet both objectives. We find that a weighted average of the two subset embeddings balances the influence of those subsets while word similarity performance decreases. We further propose a promising optimization approach to balance influences and quality of word embeddings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge