BADM: Batch ADMM for Deep Learning
Paper and Code
Jun 30, 2024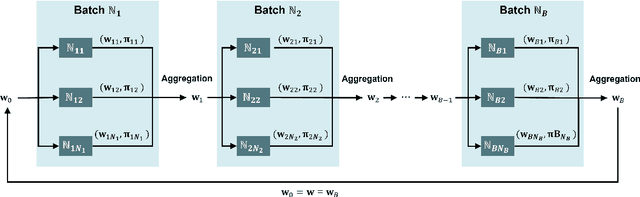
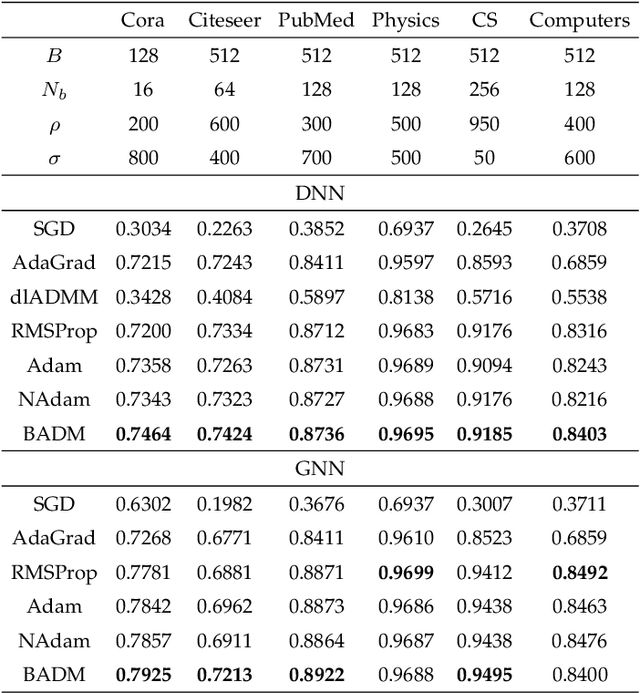
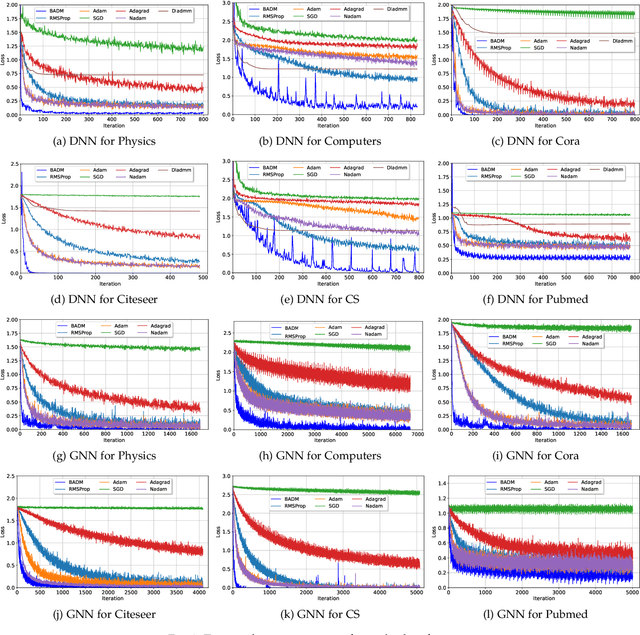
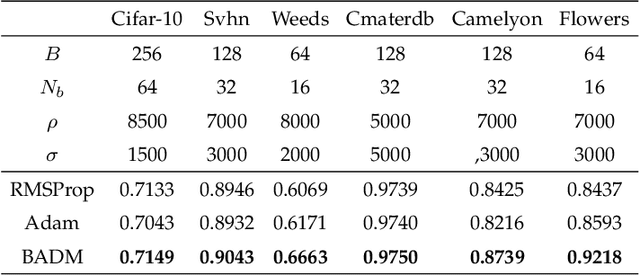
Stochastic gradient descent-based algorithms are widely used for training deep neural networks but often suffer from slow convergence. To address the challenge, we leverage the framework of the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) to develop a novel data-driven algorithm, called batch ADMM (BADM). The fundamental idea of the proposed algorithm is to split the training data into batches, which is further divided into sub-batches where primal and dual variables are updated to generate global parameters through aggregation. We evaluate the performance of BADM across various deep learning tasks, including graph modelling, computer vision, image generation, and natural language processing. Extensive numerical experiments demonstrate that BADM achieves faster convergence and superior testing accuracy compared to other state-of-the-art optimizers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge