Backhaul-Constrained Multi-Cell Cooperation Leveraging Sparsity and Spectral Clustering
Paper and Code
Oct 14, 2015
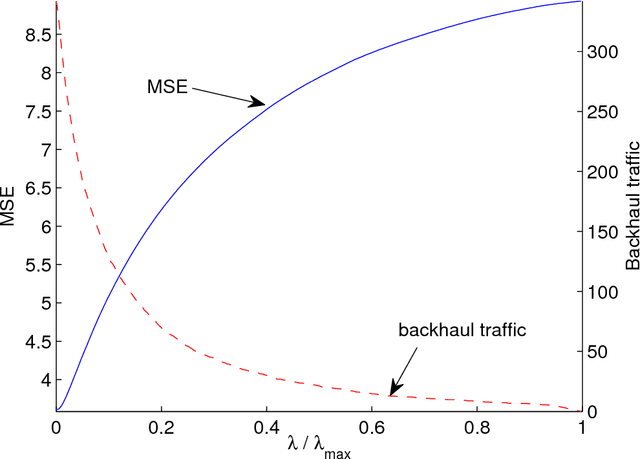


Multi-cell cooperative processing with limited backhaul traffic is studied for cellular uplinks. Aiming at reduced backhaul overhead, a sparsity-regularized multi-cell receive-filter design problem is formulated. Both unstructured distributed cooperation as well as clustered cooperation, in which base station groups are formed for tight cooperation, are considered. Dynamic clustered cooperation, where the sparse equalizer and the cooperation clusters are jointly determined, is solved via alternating minimization based on spectral clustering and group-sparse regression. Furthermore, decentralized implementations of both unstructured and clustered cooperation schemes are developed for scalability, robustness and computational efficiency. Extensive numerical tests verify the efficacy of the proposed methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge