Autoregressive Models: What Are They Good For?
Paper and Code
Oct 17, 2019
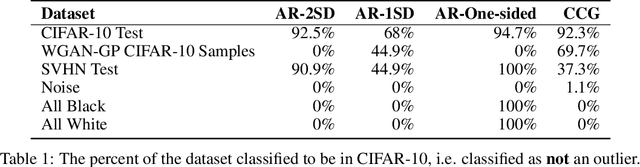


Autoregressive (AR) models have become a popular tool for unsupervised learning, achieving state-of-the-art log likelihood estimates. We investigate the use of AR models as density estimators in two settings -- as a learning signal for image translation, and as an outlier detector -- and find that these density estimates are much less reliable than previously thought. We examine the underlying optimization issues from both an empirical and theoretical perspective, and provide a toy example that illustrates the problem. Overwhelmingly, we find that density estimates do not correlate with perceptual quality and are unhelpful for downstream tasks.
* Accepted for the Information Theory and Machine Learning workshop at
NeurIPS 2019
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge