Autoregressive Co-Training for Learning Discrete Speech Representations
Paper and Code
Mar 29, 2022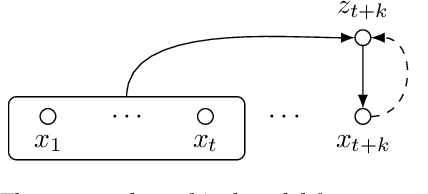
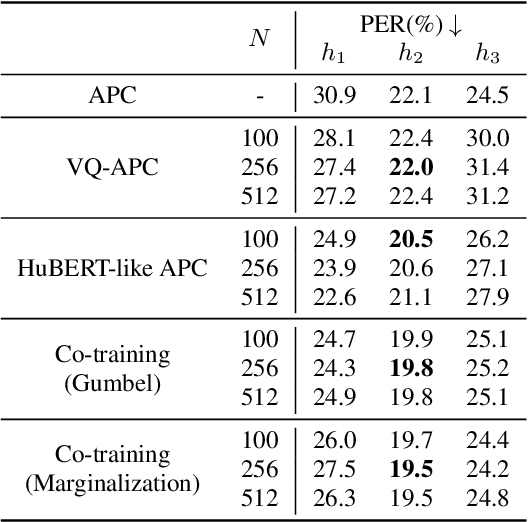
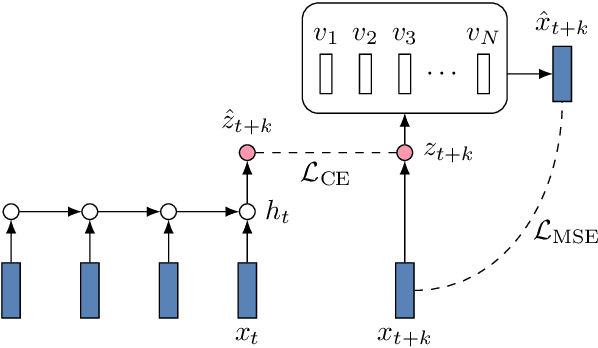
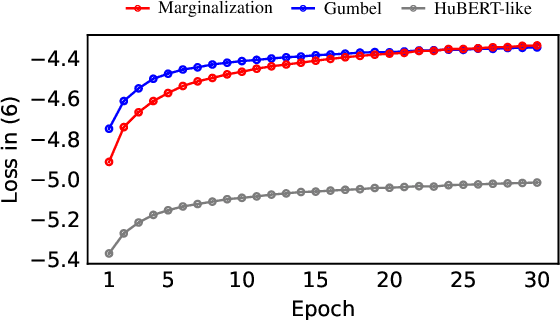
While several self-supervised approaches for learning discrete speech representation have been proposed, it is unclear how these seemingly similar approaches relate to each other. In this paper, we consider a generative model with discrete latent variables that learns a discrete representation for speech. The objective of learning the generative model is formulated as information-theoretic co-training. Besides the wide generality, the objective can be optimized with several approaches, subsuming HuBERT-like training and vector quantization for learning discrete representation. Empirically, we find that the proposed approach learns discrete representation that is highly correlated with phonetic units, more correlated than HuBERT-like training and vector quantization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge