Autonomous Navigation via Deep Reinforcement Learning for Resource Constraint Edge Nodes using Transfer Learning
Paper and Code
Oct 12, 2019
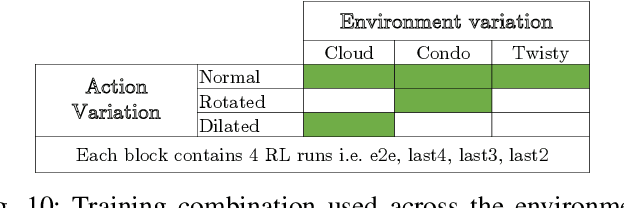
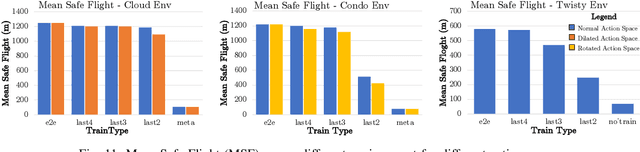
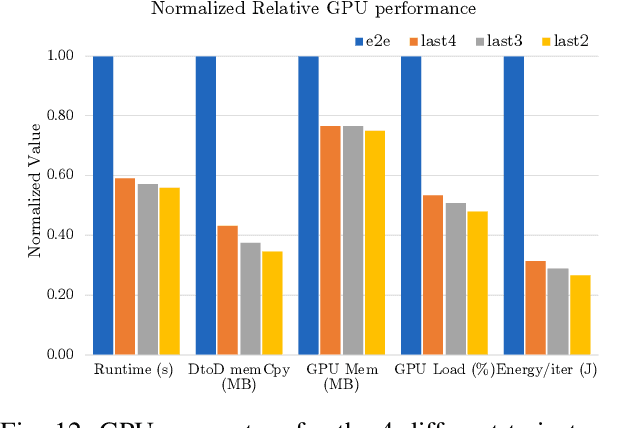
Smart and agile drones are fast becoming ubiquitous at the edge of the cloud. The usage of these drones are constrained by their limited power and compute capability. In this paper, we present a Transfer Learning (TL) based approach to reduce on-board computation required to train a deep neural network for autonomous navigation via Deep Reinforcement Learning for a target algorithmic performance. A library of 3D realistic meta-environments is manually designed using Unreal Gaming Engine and the network is trained end-to-end. These trained meta-weights are then used as initializers to the network in a test environment and fine-tuned for the last few fully connected layers. Variation in drone dynamics and environmental characteristics is carried out to show robustness of the approach. Using NVIDIA GPU profiler it was shown that the energy consumption and training latency is reduced by 3.7x and 1.8x respectively without significant degradation in the performance in terms of average distance traveled before crash i.e. Mean Safe Flight (MSF). The approach is also tested on a real environment using DJI Tello drone and similar results were reported.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge