Automatically Searching for U-Net Image Translator Architecture
Paper and Code
Feb 26, 2020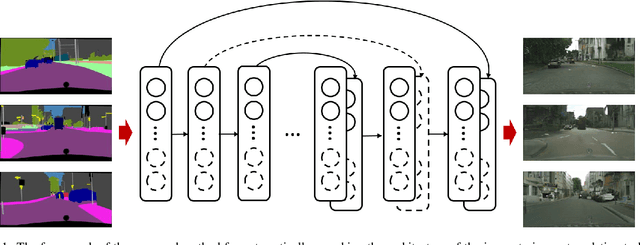
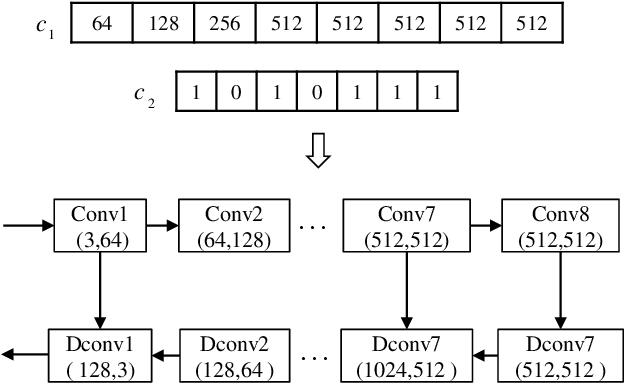

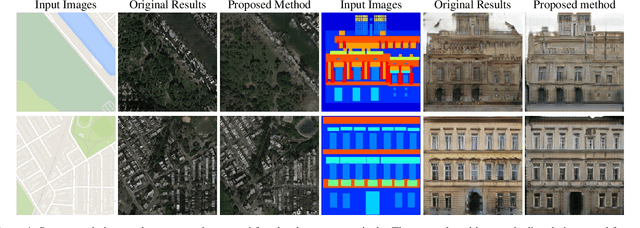
Image translators have been successfully applied to many important low level image processing tasks. However, classical network architecture of image translator like U-Net, is borrowed from other vision tasks like biomedical image segmentation. This straightforward adaptation may not be optimal and could cause redundancy in the network structure. In this paper, we propose an automatic architecture searching method for image translator. By utilizing evolutionary algorithm, we investigate a more efficient network architecture which costs less computation resources and achieves better performance than the original one. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments are conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. Moreover, we transplant the searched network architecture to other datasets which are not involved in the architecture searching procedure. Efficiency of the searched architecture on these datasets further demonstrates the generalization of the method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge