Automatically Learning Construction Injury Precursors from Text
Paper and Code
Jul 26, 2019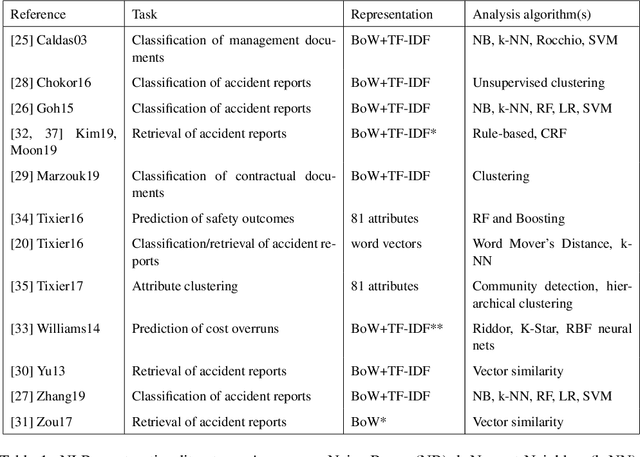
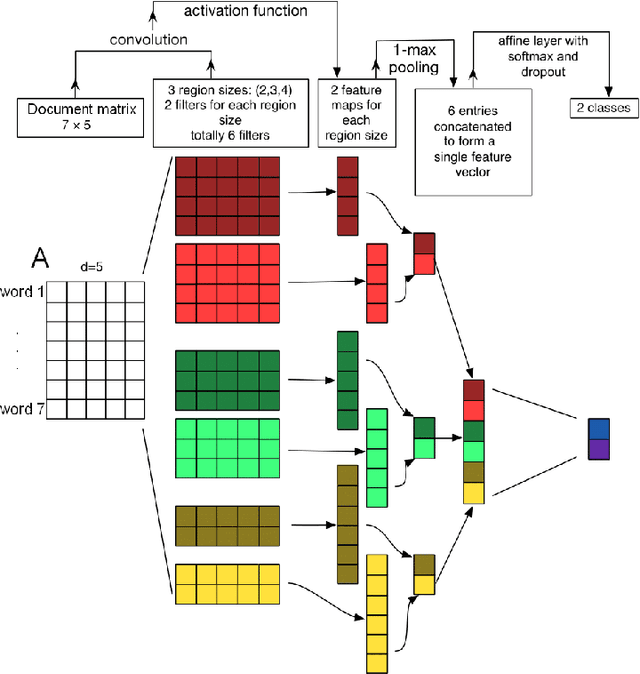
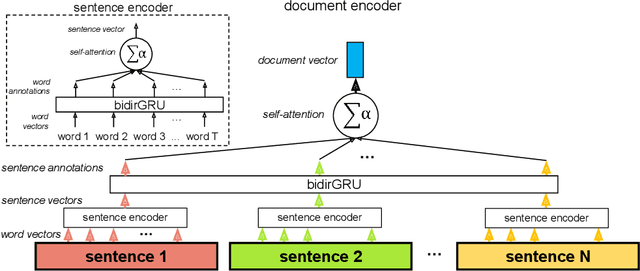
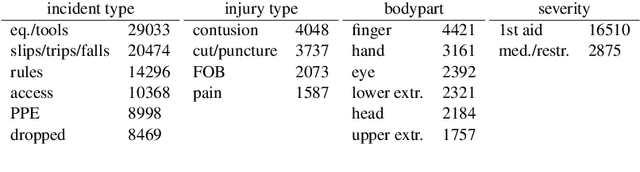
In light of the increasing availability of digitally recorded safety reports in the construction industry, it is important to develop methods to exploit these data to improve our understanding of safety incidents and ability to learn from them. In this study, we compare several approaches to automatically learn injury precursors from raw construction accident reports. More precisely, we experiment with two state-of-the-art deep learning architectures for Natural Language Processing (NLP), Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Hierarchical Attention Networks (HAN), and with the established Term Frequency - Inverse Document Frequency representation (TF-IDF) + Support Vector Machine (SVM) approach. For each model, we provide a method to identify (after training) the textual patterns that are, on average, the most predictive of each safety outcome. We show that among those pieces of text, valid injury precursors can be found. The proposed methods can also be used by the user to visualize and understand the models' predictions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge