Automatic Expansion and Retargeting of Arabic Offensive Language Training
Paper and Code
Nov 18, 2021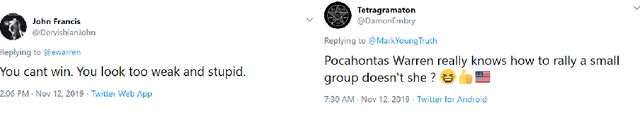
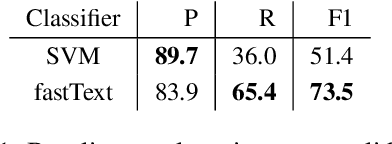
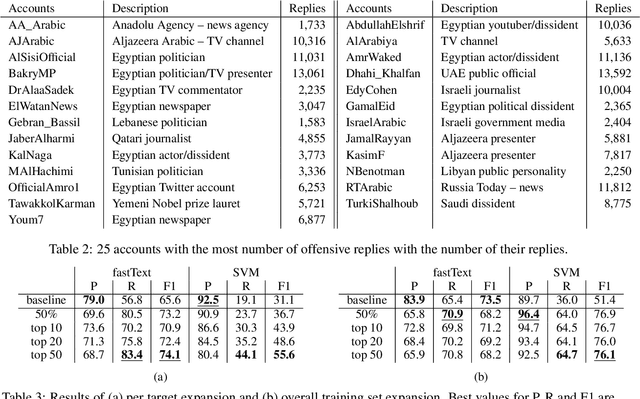
Rampant use of offensive language on social media led to recent efforts on automatic identification of such language. Though offensive language has general characteristics, attacks on specific entities may exhibit distinct phenomena such as malicious alterations in the spelling of names. In this paper, we present a method for identifying entity specific offensive language. We employ two key insights, namely that replies on Twitter often imply opposition and some accounts are persistent in their offensiveness towards specific targets. Using our methodology, we are able to collect thousands of targeted offensive tweets. We show the efficacy of the approach on Arabic tweets with 13% and 79% relative F1-measure improvement in entity specific offensive language detection when using deep-learning based and support vector machine based classifiers respectively. Further, expanding the training set with automatically identified offensive tweets directed at multiple entities can improve F1-measure by 48%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge