Automated Segmentation of Vertebrae on Lateral Chest Radiography Using Deep Learning
Paper and Code
Jan 05, 2020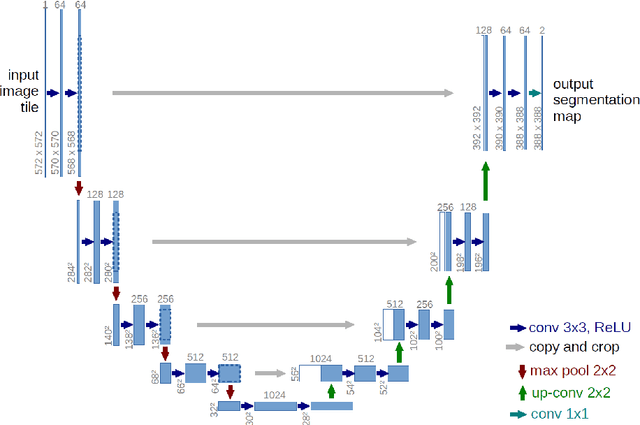
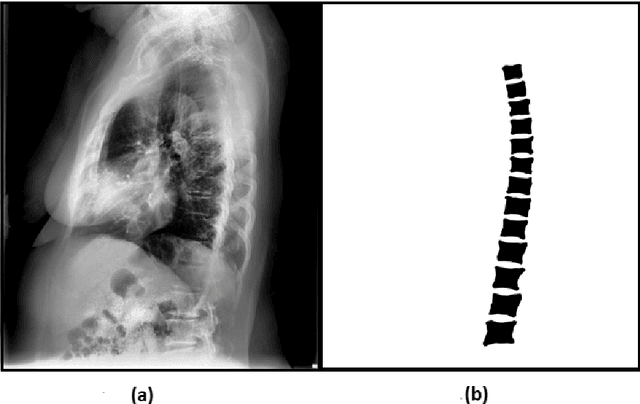
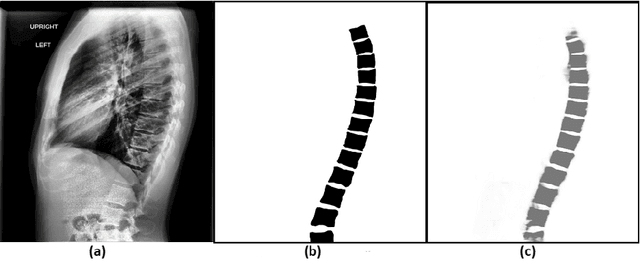
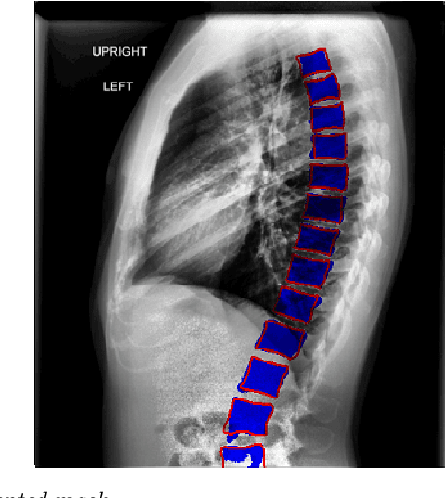
The purpose of this study is to develop an automated algorithm for thoracic vertebral segmentation on chest radiography using deep learning. 124 de-identified lateral chest radiographs on unique patients were obtained. Segmentations of visible vertebrae were manually performed by a medical student and verified by a board-certified radiologist. 74 images were used for training, 10 for validation, and 40 were held out for testing. A U-Net deep convolutional neural network was employed for segmentation, using the sum of dice coefficient and binary cross-entropy as the loss function. On the test set, the algorithm demonstrated an average dice coefficient value of 90.5 and an average intersection-over-union (IoU) of 81.75. Deep learning demonstrates promise in the segmentation of vertebrae on lateral chest radiography.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge