Automated polyp detection in colon capsule endoscopy
Paper and Code
Mar 27, 2014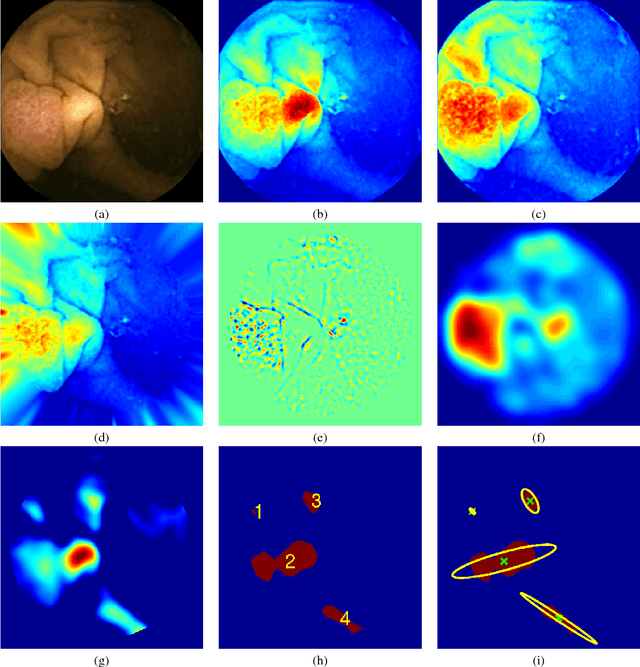
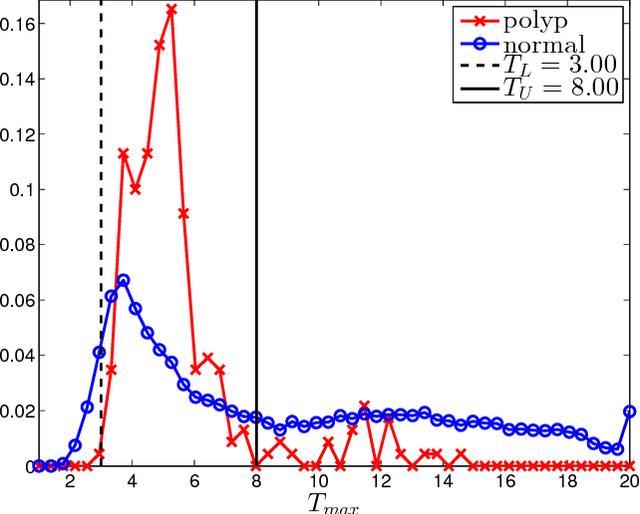
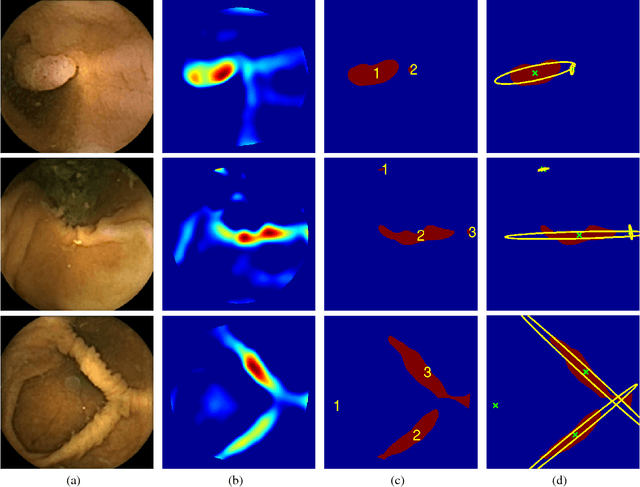
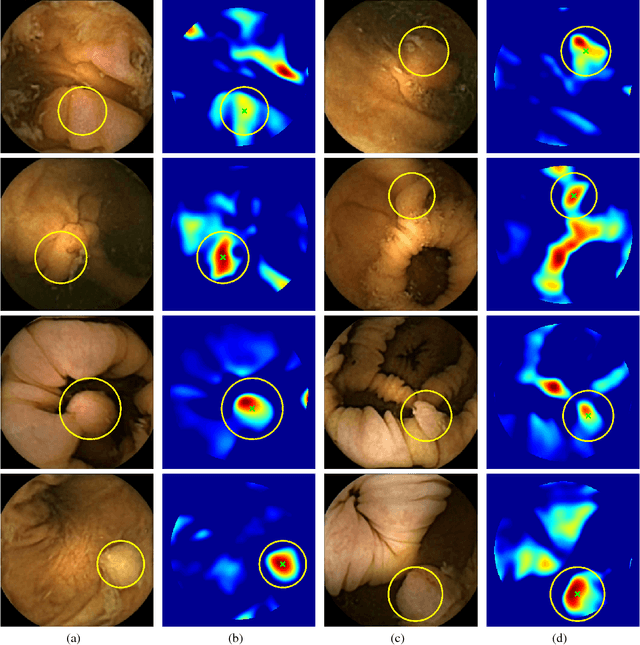
Colorectal polyps are important precursors to colon cancer, a major health problem. Colon capsule endoscopy (CCE) is a safe and minimally invasive examination procedure, in which the images of the intestine are obtained via digital cameras on board of a small capsule ingested by a patient. The video sequence is then analyzed for the presence of polyps. We propose an algorithm that relieves the labor of a human operator analyzing the frames in the video sequence. The algorithm acts as a binary classifier, which labels the frame as either containing polyps or not, based on the geometrical analysis and the texture content of the frame. The geometrical analysis is based on a segmentation of an image with the help of a mid-pass filter. The features extracted by the segmentation procedure are classified according to an assumption that the polyps are characterized as protrusions that are mostly round in shape. Thus, we use a best fit ball radius as a decision parameter of a binary classifier. We present a statistical study of the performance of our approach on a data set containing over 18,900 frames from the endoscopic video sequences of five adult patients. The algorithm demonstrates a solid performance, achieving 47% sensitivity per frame and over 81% sensitivity per polyp at a specificity level of 90%. On average, with a video sequence length of 3747 frames, only 367 false positive frames need to be inspected by a human operator.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge