Automated Generation of Reactive Programs from Human Demonstration for Orchestration of Robot Behaviors
Paper and Code
Mar 13, 2019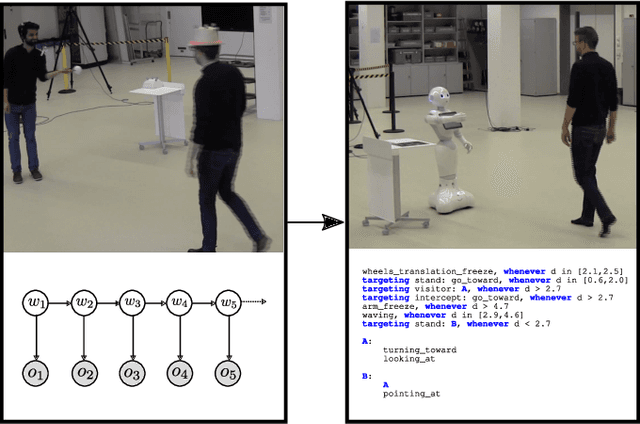
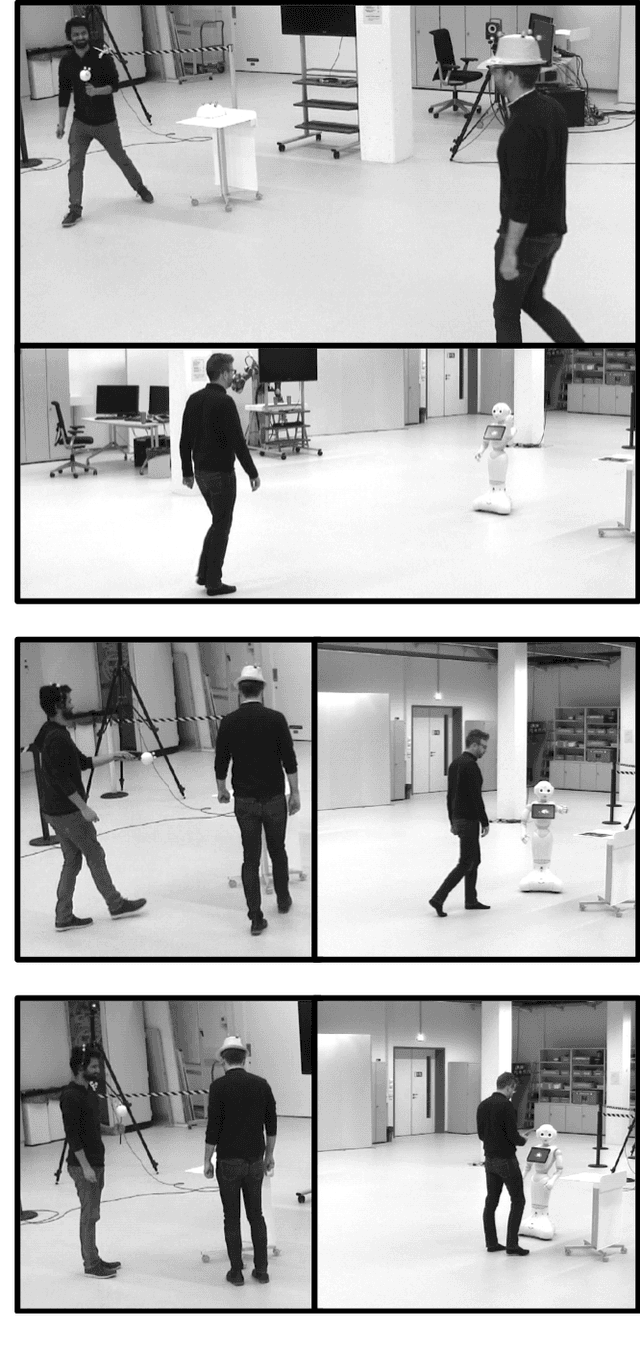
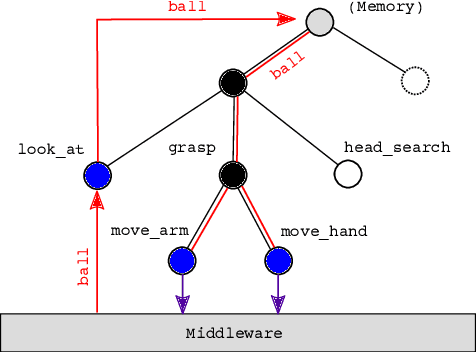
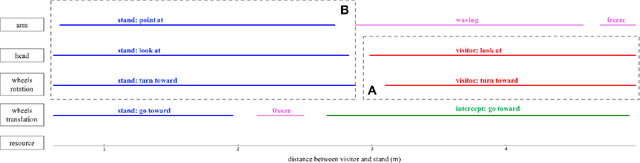

Social robots or collaborative robots that have to interact with people in a reactive way are difficult to program. This difficulty stems from the different skills required by the programmer: to provide an engaging user experience the behavior must include a sense of aesthetics while robustly operating in a continuously changing environment. The Playful framework allows composing such dynamic behaviors using a basic set of action and perception primitives. Within this framework, a behavior is encoded as a list of declarative statements corresponding to high-level sensory-motor couplings. To facilitate non-expert users to program such behaviors, we propose a Learning from Demonstration (LfD) technique that maps motion capture of humans directly to a Playful script. The approach proceeds by identifying the sensory-motor couplings that are active at each step using the Viterbi path in a Hidden Markov Model (HMM). Given these activation patterns, binary classifiers called evaluations are trained to associate activations to sensory data. Modularity is increased by clustering the sensory-motor couplings, leading to a hierarchical tree structure. The novelty of the proposed approach is that the learned behavior is encoded not in terms of trajectories in a task space, but as couplings between sensory information and high-level motor actions. This provides advantages in terms of behavioral generalization and reactivity displayed by the robot.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge