Attention-Based Keyword Localisation in Speech using Visual Grounding
Paper and Code
Jun 23, 2021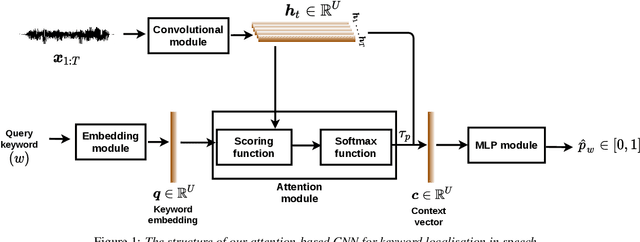
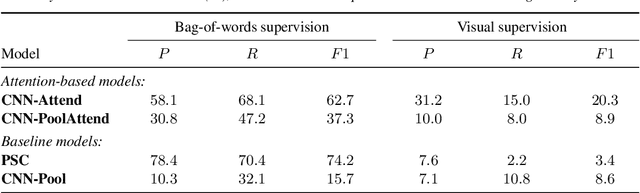
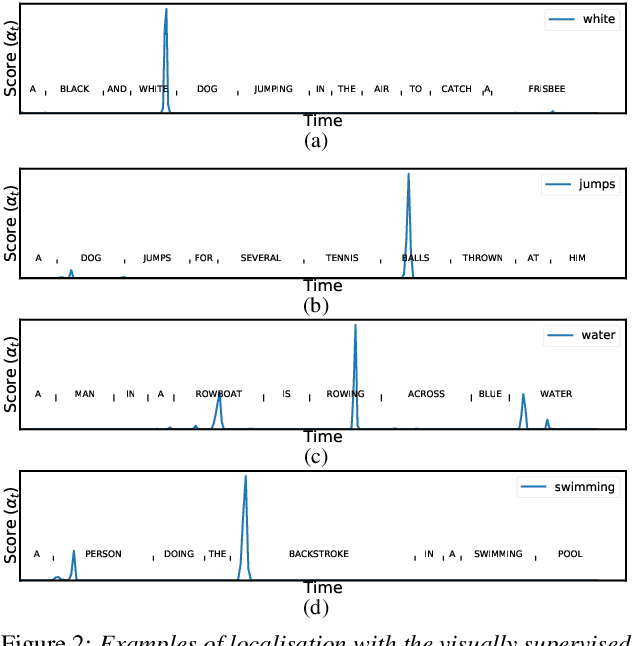
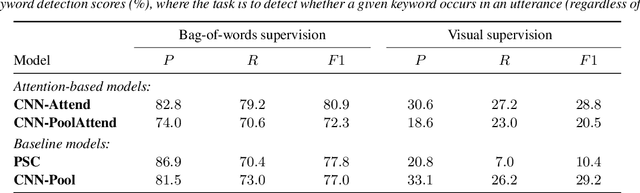
Visually grounded speech models learn from images paired with spoken captions. By tagging images with soft text labels using a trained visual classifier with a fixed vocabulary, previous work has shown that it is possible to train a model that can detect whether a particular text keyword occurs in speech utterances or not. Here we investigate whether visually grounded speech models can also do keyword localisation: predicting where, within an utterance, a given textual keyword occurs without any explicit text-based or alignment supervision. We specifically consider whether incorporating attention into a convolutional model is beneficial for localisation. Although absolute localisation performance with visually supervised models is still modest (compared to using unordered bag-of-word text labels for supervision), we show that attention provides a large gain in performance over previous visually grounded models. As in many other speech-image studies, we find that many of the incorrect localisations are due to semantic confusions, e.g. locating the word 'backstroke' for the query keyword 'swimming'.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge