ARTiS: Appearance-based Action Recognition in Task Space for Real-Time Human-Robot Collaboration
Paper and Code
Mar 07, 2017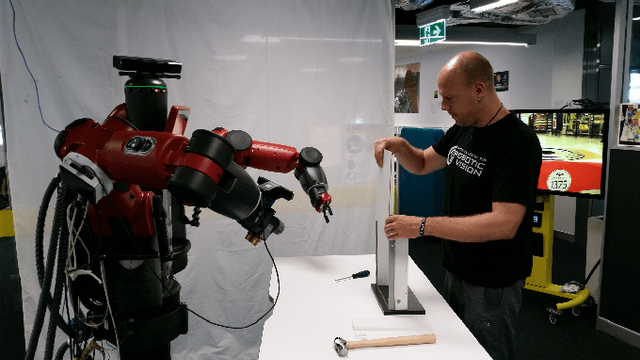
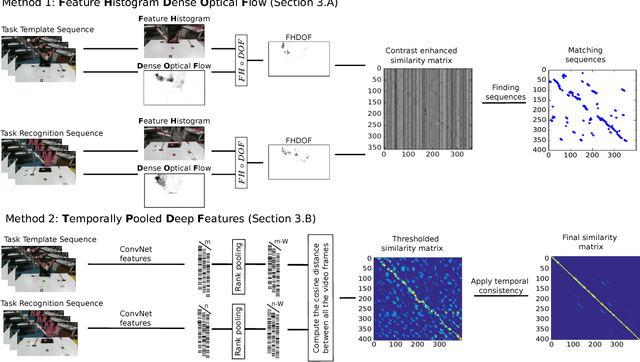
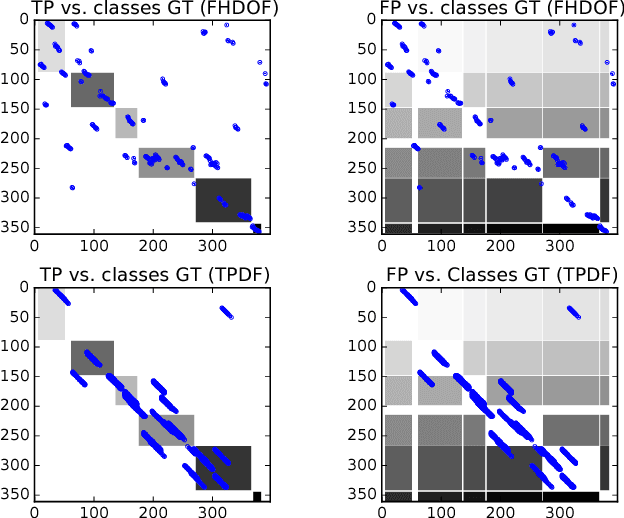
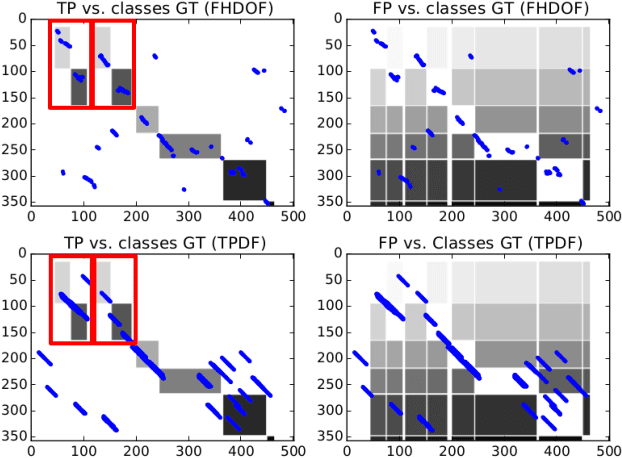
To have a robot actively supporting a human during a collaborative task, it is crucial that robots are able to identify the current action in order to predict the next one. Common approaches make use of high-level knowledge, such as object affordances, semantics or understanding of actions in terms of pre- and post-conditions. These approaches often require hand-coded a priori knowledge, time- and resource-intensive or supervised learning techniques. We propose to reframe this problem as an appearance-based place recognition problem. In our framework, we regard sequences of visual images of human actions as a map in analogy to the visual place recognition problem. Observing the task for the second time, our approach is able to recognize pre-observed actions in a one-shot learning approach and is thereby able to recognize the current observation in the task space. We propose two new methods for creating and aligning action observations within a task map. We compare and verify our approaches with real data of humans assembling several types of IKEA flat packs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge