Approximate Maximum Likelihood Inference for Acoustic Spatial Capture-Recapture with Unknown Identities, Using Monte Carlo Expectation Maximization
Paper and Code
Oct 06, 2024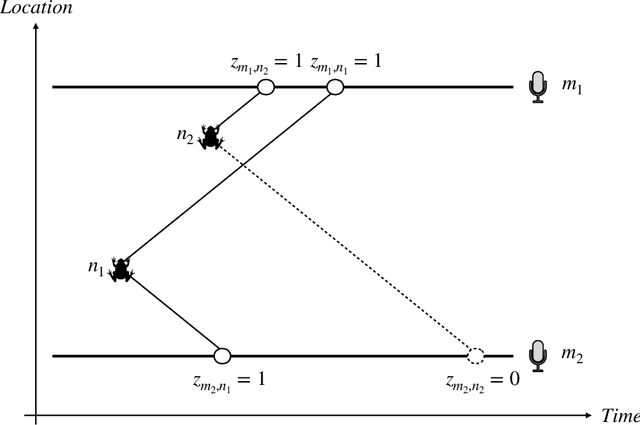
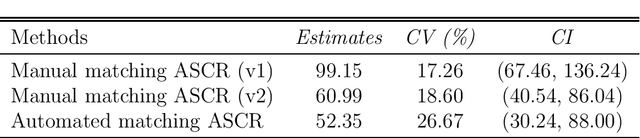
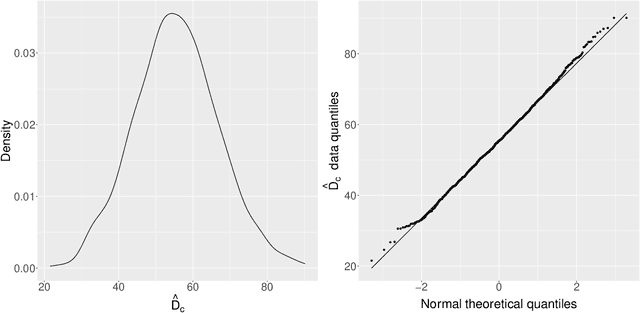

Acoustic spatial capture-recapture (ASCR) surveys with an array of synchronized acoustic detectors can be an effective way of estimating animal density or call density. However, constructing the capture histories required for ASCR analysis is challenging, as recognizing which detections at different detectors are of which calls is not a trivial task. Because calls from different distances take different times to arrive at detectors, the order in which calls are detected is not necessarily the same as the order in which they are made, and without knowing which detections are of the same call, we do not know how many different calls are detected. We propose a Monte Carlo expectation-maximization (MCEM) estimation method to resolve this unknown call identity problem. To implement the MCEM method in this context, we sample the latent variables from a complete-data likelihood model in the expectation step and use a semi-complete-data likelihood or conditional likelihood in the maximization step. We use a parametric bootstrap to obtain confidence intervals. When we apply our method to a survey of moss frogs, it gives an estimate within 15% of the estimate obtained using data with call capture histories constructed by experts, and unlike this latter estimate, our confidence interval incorporates the uncertainty about call identities. Simulations show it to have a low bias (6%) and coverage probabilities close to the nominal 95% value.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge