Approximate inference with Wasserstein gradient flows
Paper and Code
Jun 12, 2018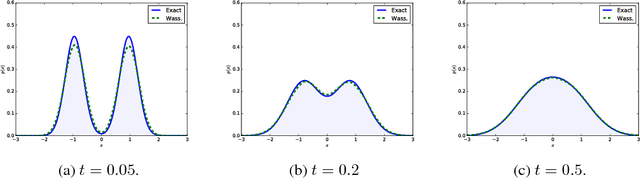
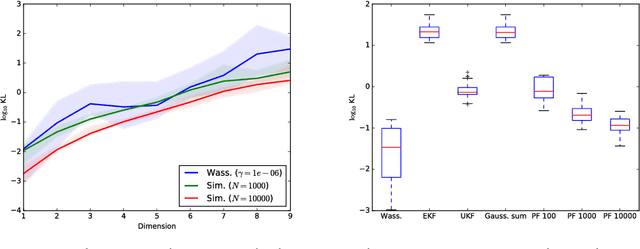
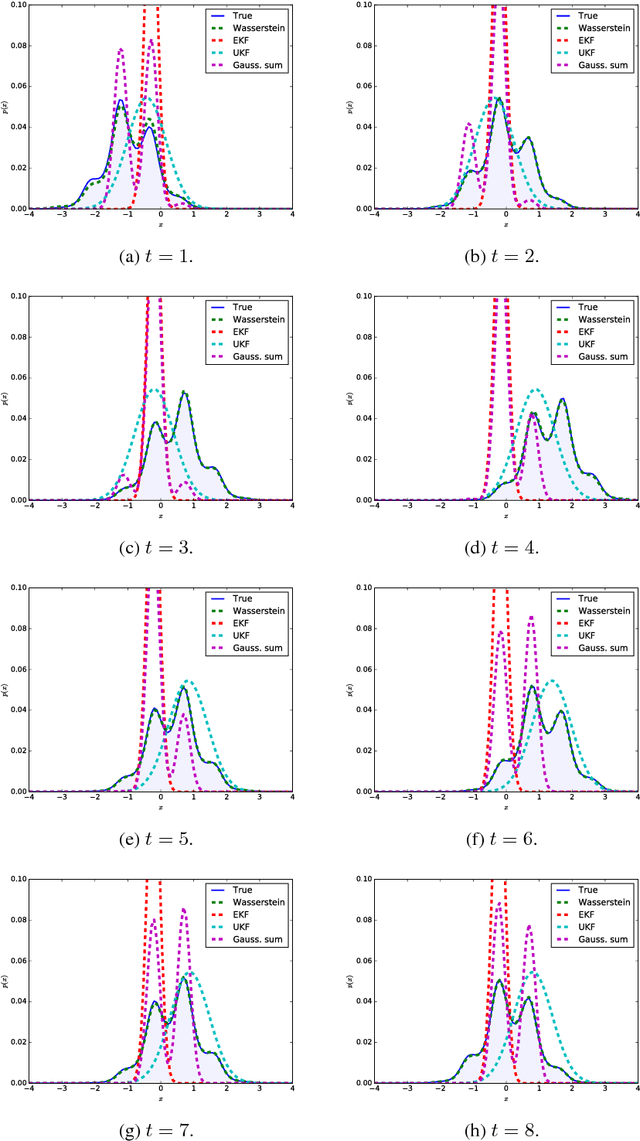
We present a novel approximate inference method for diffusion processes, based on the Wasserstein gradient flow formulation of the diffusion. In this formulation, the time-dependent density of the diffusion is derived as the limit of implicit Euler steps that follow the gradients of a particular free energy functional. Existing methods for computing Wasserstein gradient flows rely on discretization of the domain of the diffusion, prohibiting their application to domains in more than several dimensions. We propose instead a discretization-free inference method that computes the Wasserstein gradient flow directly in a space of continuous functions. We characterize approximation properties of the proposed method and evaluate it on a nonlinear filtering task, finding performance comparable to the state-of-the-art for filtering diffusions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge