Anisotropic Multi-Scale Graph Convolutional Network for Dense Shape Correspondence
Paper and Code
Oct 17, 2022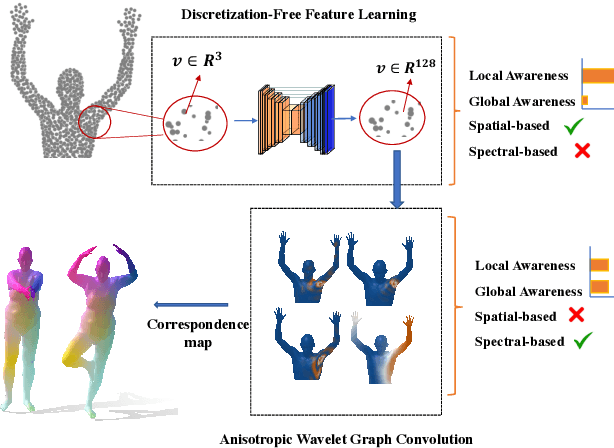
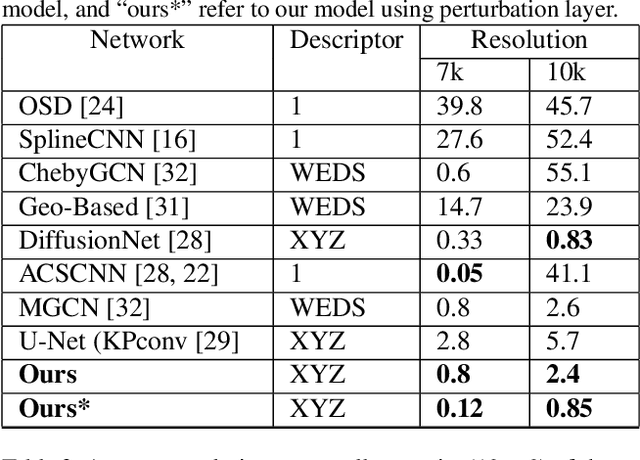
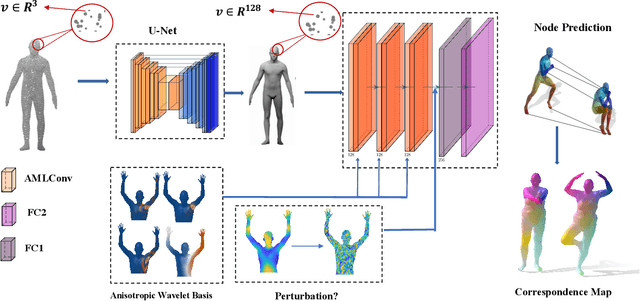

This paper studies 3D dense shape correspondence, a key shape analysis application in computer vision and graphics. We introduce a novel hybrid geometric deep learning-based model that learns geometrically meaningful and discretization-independent features with a U-Net model as the primary node feature extraction module, followed by a successive spectral-based graph convolutional network. To create a diverse set of filters, we use anisotropic wavelet basis filters, being sensitive to both different directions and band-passes. This filter set overcomes the over-smoothing behavior of conventional graph neural networks. To further improve the model's performance, we add a function that perturbs the feature maps in the last layer ahead of fully connected layers, forcing the network to learn more discriminative features overall. The resulting correspondence maps show state-of-the-art performance on the benchmark datasets based on average geodesic errors and superior robustness to discretization in 3D meshes. Our approach provides new insights and practical solutions to the dense shape correspondence research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge