Anatomical Mesh-Based Virtual Fixtures for Surgical Robots
Paper and Code
Jun 03, 2020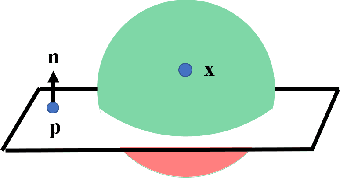
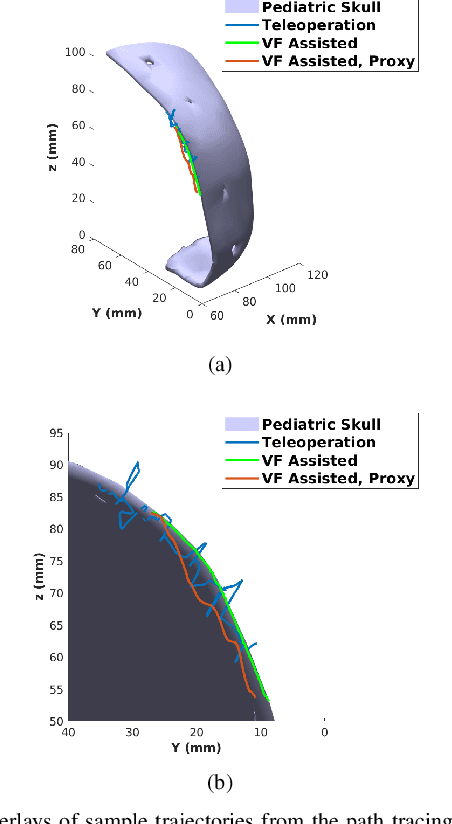

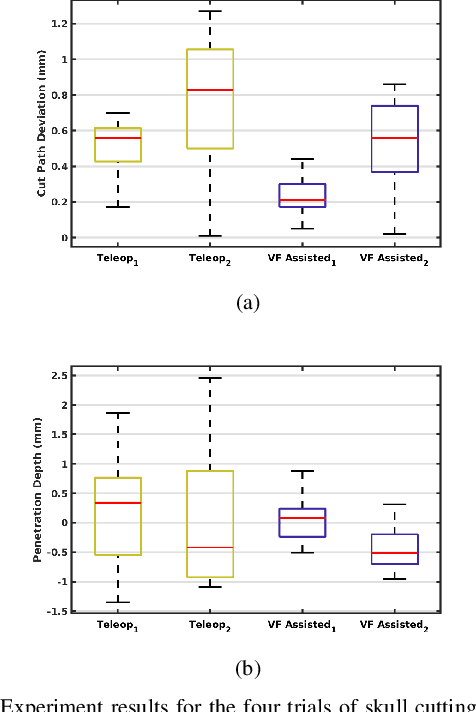
This paper presents a dynamic constraint formulation to provide protective virtual fixtures of 3D anatomical structures from polygon mesh representations. The proposed approach can anisotropically limit the tool motion of surgical robots without any assumption of the local anatomical shape close to the tool. Using a bounded search strategy and Principle Directed tree, the proposed system can run efficiently at 180 Hz for a mesh object containing 989,376 triangles and 493,460 vertices. The proposed algorithm has been validated in both simulation and skull cutting experiments. The skull cutting experiment setup uses a novel piezoelectric bone cutting tool designed for the da Vinci research kit. The result shows that the virtual fixture assisted teleoperation has statistically significant improvements in the cutting path accuracy and penetration depth control.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge