Analyzing the Robustness of PECNet
Paper and Code
Oct 15, 2022
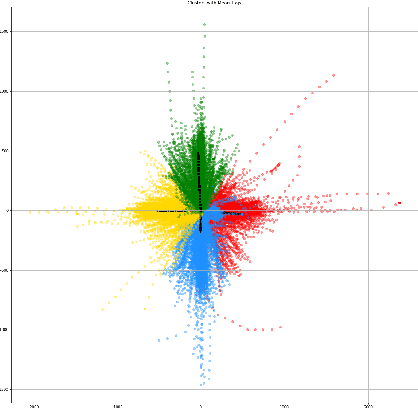
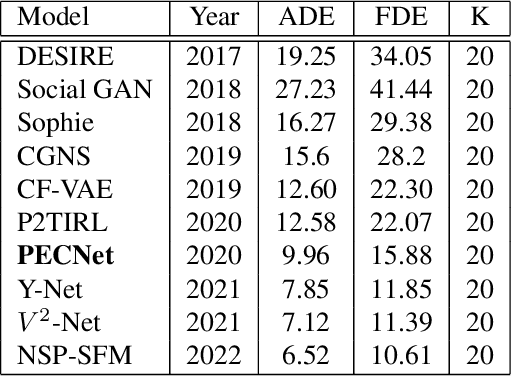
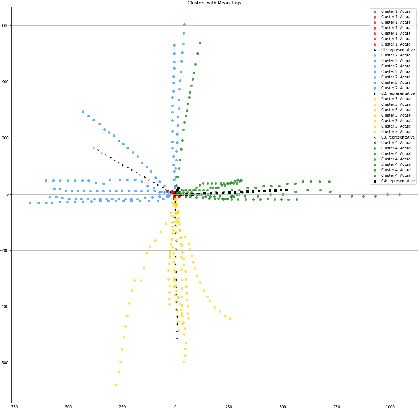
Comprehensive robustness analysis of PECNet, a pedestrian trajectory prediction system for autonomous vehicles. A novel metric is introduced for dataset analysis and classification. Synthetic data augmentation techniques ranging from Newtonian mechanics to Deep Reinforcement Learning based simulations are used to improve and test the system. An improvement of 9.5% over state-of-the-art results is seen on the FDE while compromising ADE. We introduce novel architectural changes using SIRENs for higher precision results to validate our robustness hypotheses. Additionally, we diagrammatically propose a novel multi-modal system for the same task.
* 13 pages, 17 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge