Analysis of Rigid Extended Object Co-Manipulation by Human Dyads: Lateral Movement Characterization
Paper and Code
Feb 02, 2017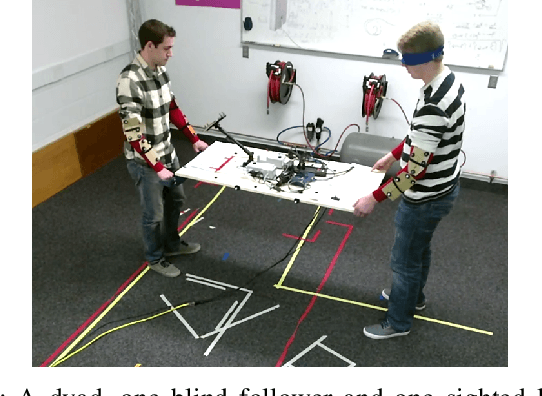
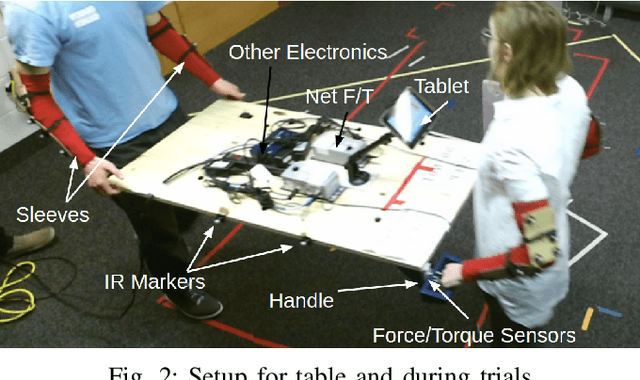
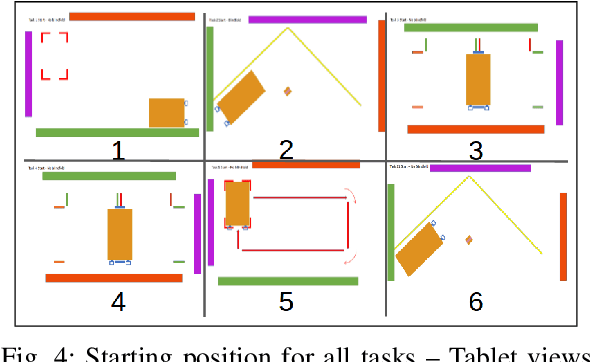
During co-manipulation involving humans and robots, it is necessary to base robot controllers on human behaviors to achieve comfortable and coordinated movement between the human-robot dyad. In this paper, we describe an experiment between human-human dyads and we record the force and motion data as the leader-follower dyads moved in translation and rotation. The force/motion data was then analyzed for patterns found during lateral translation only. For extended objects, lateral translation and in-place rotation are ambiguous, but this paper determines a way to characterize lateral translation triggers for future use in human-robot interaction. The study has 4 main results. First, interaction forces are apparent and necessary for co-manipulation. Second, minimum-jerk trajectories are found in the lateral direction only for lateral movement. Third, the beginning of a lateral movement is characterized by distinct force triggers by the leader. Last, there are different metrics that can be attributed to determine which dyads moved most effectively in the lateral direction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge