Analysis and development of a novel algorithm for the in-vehicle hand-usage of a smartphone
Paper and Code
Aug 30, 2018
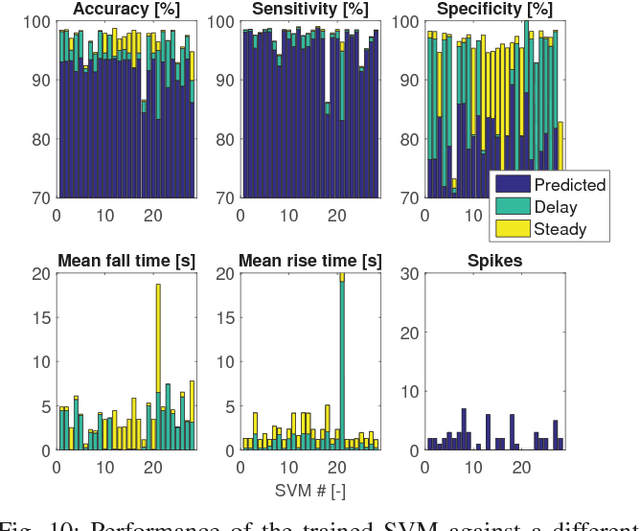
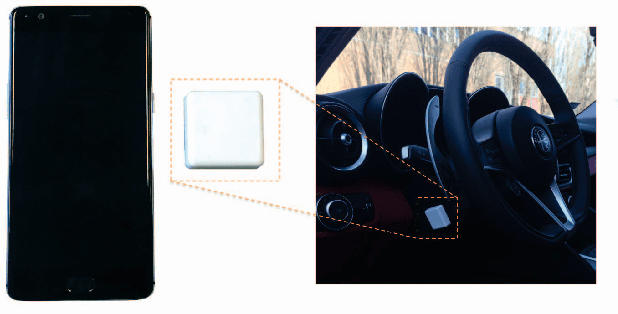
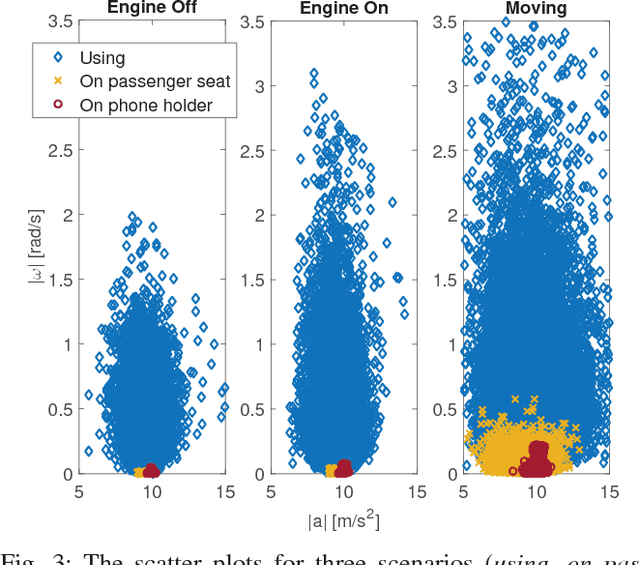
Smartphone usage while driving is unanimously considered to be a really dangerous habit due to strong correlation with road accidents. In this paper, the problem of detecting whether the driver is using the phone during a trip is addressed. To do this, high-frequency data from the triaxial inertial measurement unit (IMU) integrated in almost all modern phone is processed without relying on external inputs so as to provide a self-contained approach. By resorting to a frequency-domain analysis, it is possible to extract from the raw signals the useful information needed to detect when the driver is using the phone, without being affected by the effects that vehicle motion has on the same signals. The selected features are used to train a Support Vector Machine (SVM) algorithm. The performance of the proposed approach are analyzed and tested on experimental data collected during mixed naturalistic driving scenarios, proving the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge