An optimal approximation of discrete random variables with respect to the Kolmogorov distance
Paper and Code
May 19, 2018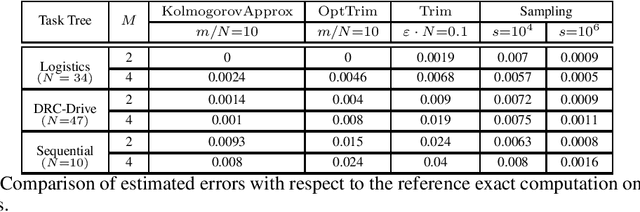
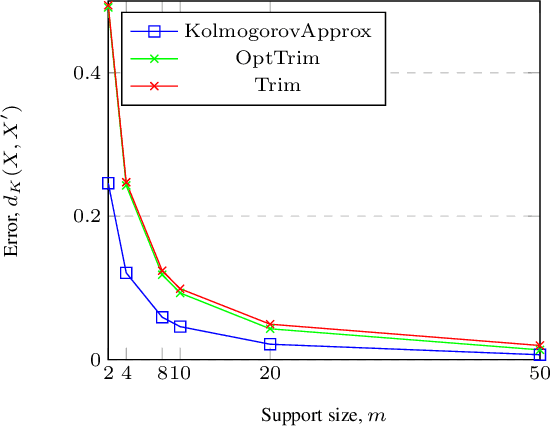
We present an algorithm that takes a discrete random variable $X$ and a number $m$ and computes a random variable whose support (set of possible outcomes) is of size at most $m$ and whose Kolmogorov distance from $X$ is minimal. In addition to a formal theoretical analysis of the correctness and of the computational complexity of the algorithm, we present a detailed empirical evaluation that shows how the proposed approach performs in practice in different applications and domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge