An Explainable Stacked Ensemble Model for Static Route-Free Estimation of Time of Arrival
Paper and Code
Mar 17, 2022

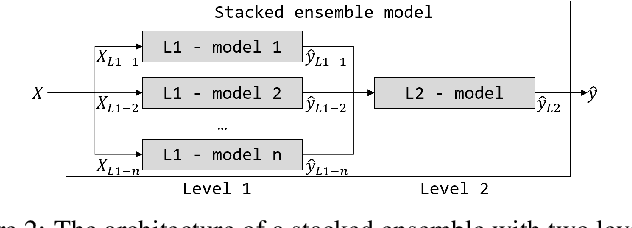
To compare alternative taxi schedules and to compute them, as well as to provide insights into an upcoming taxi trip to drivers and passengers, the duration of a trip or its Estimated Time of Arrival (ETA) is predicted. To reach a high prediction precision, machine learning models for ETA are state of the art. One yet unexploited option to further increase prediction precision is to combine multiple ETA models into an ensemble. While an increase of prediction precision is likely, the main drawback is that the predictions made by such an ensemble become less transparent due to the sophisticated ensemble architecture. One option to remedy this drawback is to apply eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI). The contribution of this paper is three-fold. First, we combine multiple machine learning models from our previous work for ETA into a two-level ensemble model - a stacked ensemble model - which on its own is novel; therefore, we can outperform previous state-of-the-art static route-free ETA approaches. Second, we apply existing XAI methods to explain the first- and second-level models of the ensemble. Third, we propose three joining methods for combining the first-level explanations with the second-level ones. Those joining methods enable us to explain stacked ensembles for regression tasks. An experimental evaluation shows that the ETA models correctly learned the importance of those input features driving the prediction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge