An End-to-End Robot Architecture to Manipulate Non-Physical State Changes of Objects
Paper and Code
Sep 27, 2016

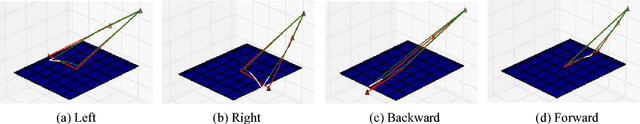
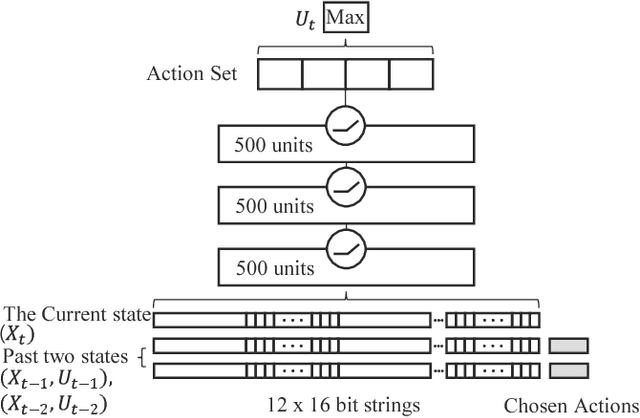
With the advance in robotic hardware and intelligent software, humanoid robot plays an important role in various tasks including service for human assistance and heavy job for hazardous industry. Recent advances in task learning enable humanoid robots to conduct dexterous manipulation tasks such as grasping objects and assembling parts of furniture. Operating objects without physical movements is an even more challenging task for humanoid robot because effects of actions may not be clearly seen in the physical configuration space and meaningful actions could be very complex in a long time horizon. As an example, playing a mobile game in a smart device has such challenges because both swipe actions and complex state transitions inside the smart devices in a long time horizon. In this paper, we solve this problem by introducing an integrated architecture which connects end-to-end dataflow from sensors to actuators in a humanoid robot to operate smart devices. We implement our integrated architecture in the Baxter Research Robot and experimentally demonstrate that the robot with our architecture could play a challenging mobile game, the 2048 game, as accurate as in a simulated environment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge