An Empirical Study on Internet Traffic Prediction Using Statistical Rolling Model
Paper and Code
May 03, 2022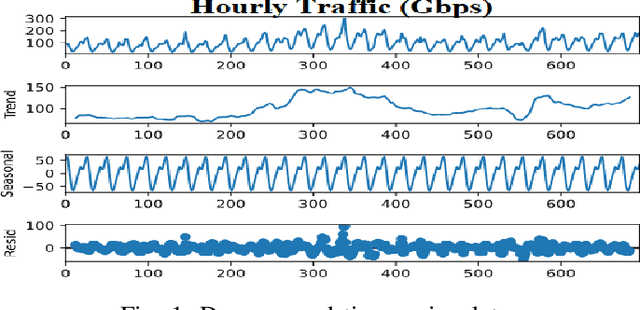
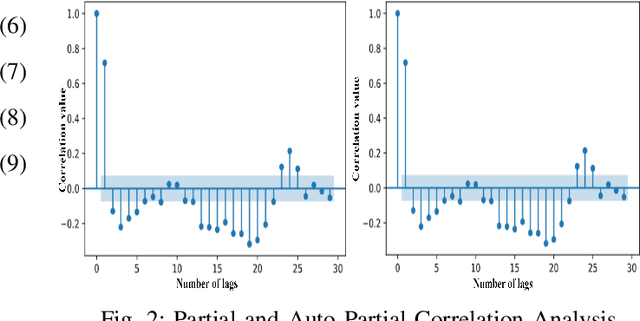
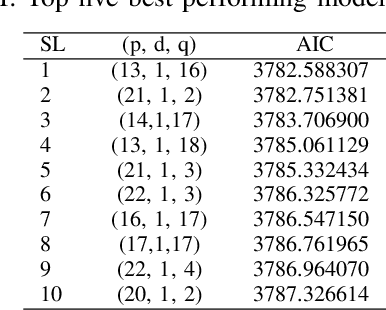
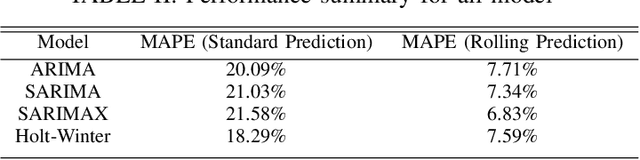
Real-world IP network traffic is susceptible to external and internal factors such as new internet service integration, traffic migration, internet application, etc. Due to these factors, the actual internet traffic is non-linear and challenging to analyze using a statistical model for future prediction. In this paper, we investigated and evaluated the performance of different statistical prediction models for real IP network traffic; and showed a significant improvement in prediction using the rolling prediction technique. Initially, a set of best hyper-parameters for the corresponding prediction model is identified by analyzing the traffic characteristics and implementing a grid search algorithm based on the minimum Akaike Information Criterion (AIC). Then, we performed a comparative performance analysis among AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA), Seasonal ARIMA (SARIMA), SARIMA with eXogenous factors (SARIMAX), and Holt-Winter for single-step prediction. The seasonality of our traffic has been explicitly modeled using SARIMA, which reduces the rolling prediction Mean Average Percentage Error (MAPE) by more than 4% compared to ARIMA (incapable of handling the seasonality). We further improved traffic prediction using SARIMAX to learn different exogenous factors extracted from the original traffic, which yielded the best rolling prediction results with a MAPE of 6.83%. Finally, we applied the exponential smoothing technique to handle the variability in traffic following the Holt-Winter model, which exhibited a better prediction than ARIMA (around 1.5% less MAPE). The rolling prediction technique reduced prediction error using real Internet Service Provider (ISP) traffic data by more than 50\% compared to the standard prediction method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge