An Electrocommunication System Using FSK Modulation and Deep Learning Based Demodulation for Underwater Robots
Paper and Code
Aug 24, 2020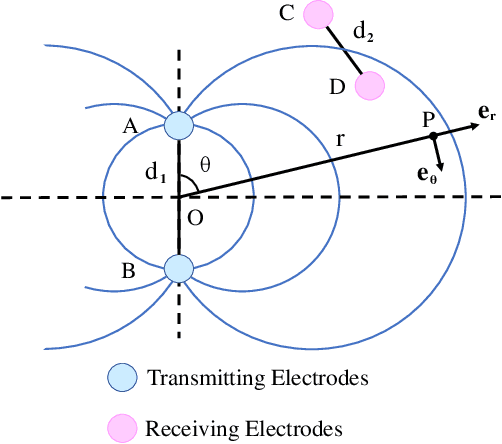
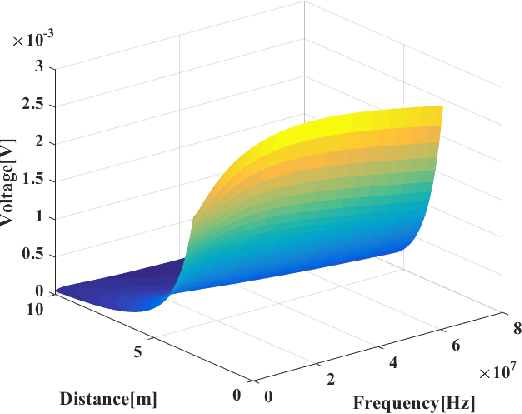
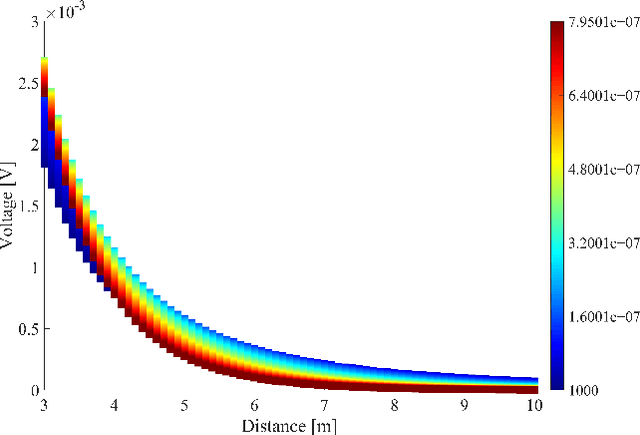
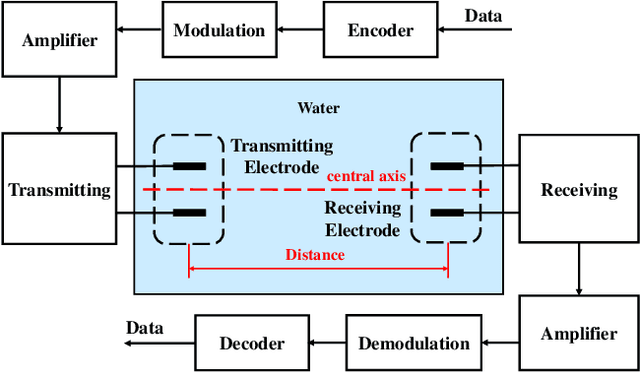
Underwater communication is extremely challenging for small underwater robots which typically have stringent power and size constraints. In our previous work, we developed an artificial electrocommunication system which could be an alternative for the communication of small underwater robots. This paper further presents a new electrocommunication system that utilizes Binary Frequency Shift Keying (2FSK) modulation and deep-learning-based demodulation for underwater robots. We first derive an underwater electrocommunication model that covers both the near-field area and a large transition area outside of the near-field area. 2FSK modulation is adopted to improve the anti-interference ability of the electric signal. A deep learning algorithm is used to demodulate the electric signal by the receiver. Simulations and experiments show that with the same testing condition, the new communication system outperforms the previous system in both the communication distance and the data transmitting rate. In specific, the newly developed communication system achieves stable communication within the distance of 10 m at a data transfer rate of 5 Kbps with a power consumption of less than 0.1 W. The substantial increase in communication distance further improves the possibility of electrocommunication in underwater robotics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge