An Analysis of Pre-Training on Object Detection
Paper and Code
Apr 11, 2019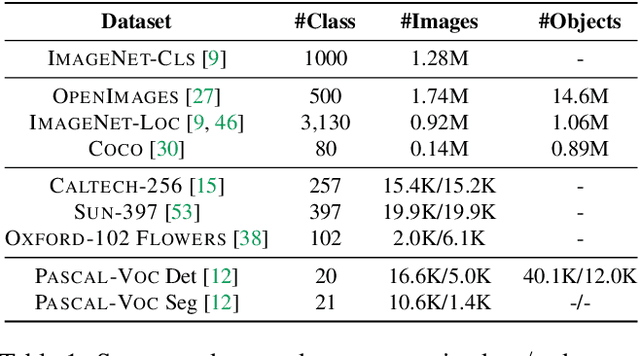
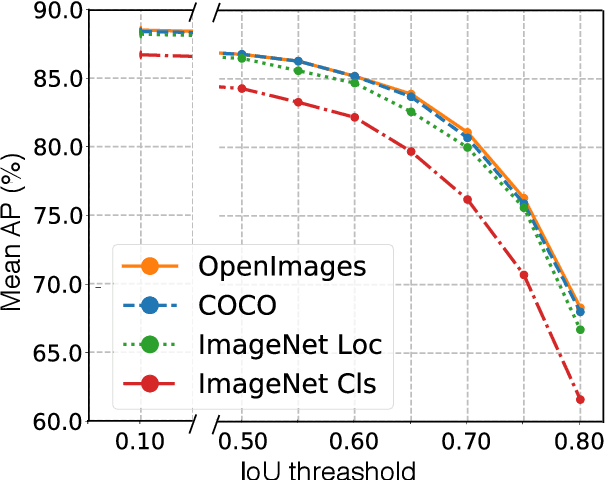
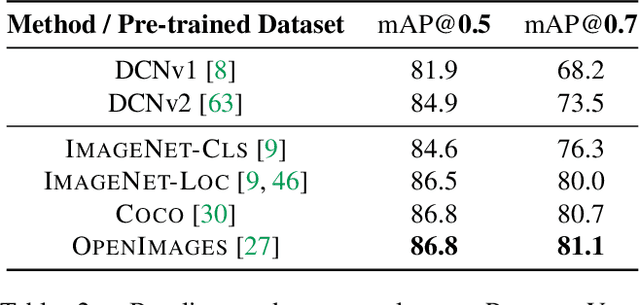
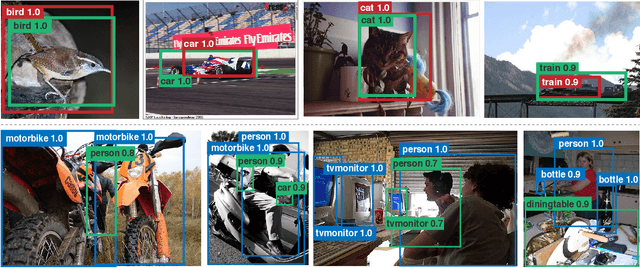
We provide a detailed analysis of convolutional neural networks which are pre-trained on the task of object detection. To this end, we train detectors on large datasets like OpenImagesV4, ImageNet Localization and COCO. We analyze how well their features generalize to tasks like image classification, semantic segmentation and object detection on small datasets like PASCAL-VOC, Caltech-256, SUN-397, Flowers-102 etc. Some important conclusions from our analysis are --- 1) Pre-training on large detection datasets is crucial for fine-tuning on small detection datasets, especially when precise localization is needed. For example, we obtain 81.1% mAP on the PASCAL-VOC dataset at 0.7 IoU after pre-training on OpenImagesV4, which is 7.6% better than the recently proposed DeformableConvNetsV2 which uses ImageNet pre-training. 2) Detection pre-training also benefits other localization tasks like semantic segmentation but adversely affects image classification. 3) Features for images (like avg. pooled Conv5) which are similar in the object detection feature space are likely to be similar in the image classification feature space but the converse is not true. 4) Visualization of features reveals that detection neurons have activations over an entire object, while activations for classification networks typically focus on parts. Therefore, detection networks are poor at classification when multiple instances are present in an image or when an instance only covers a small fraction of an image.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge