AmbiSep: Ambisonic-to-Ambisonic Reverberant Speech Separation Using Transformer Networks
Paper and Code
Jun 13, 2022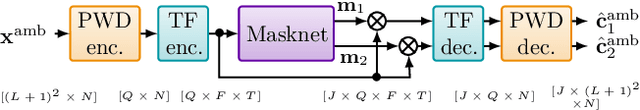
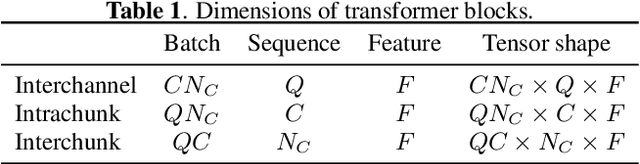
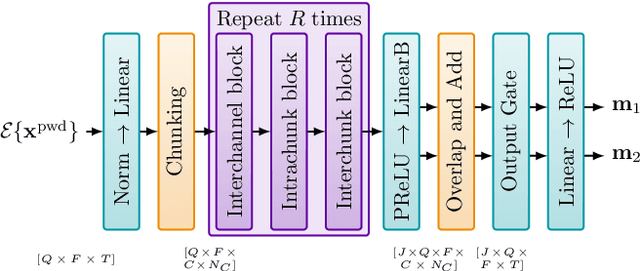
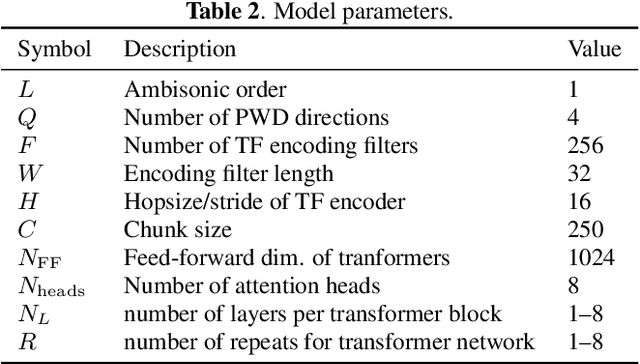
Consider a multichannel Ambisonic recording containing a mixture of several reverberant speech signals. Retreiving the reverberant Ambisonic signals corresponding to the individual speech sources blindly from the mixture is a challenging task as it requires to estimate multiple signal channels for each source. In this work, we propose AmbiSep, a deep neural network-based plane-wave domain masking approach to solve this task. The masking network uses learned feature representations and transformers in a triple-path processing configuration. We train and evaluate the proposed network architecture on a spatialized WSJ0-2mix dataset, and show that the method achieves a multichannel scale-invariant signal-to-distortion ratio improvement of 17.7 dB on the blind test set, while preserving the spatial characteristics of the separated sounds.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge