Alpha/Beta Divergences and Tweedie Models
Paper and Code
Sep 19, 2012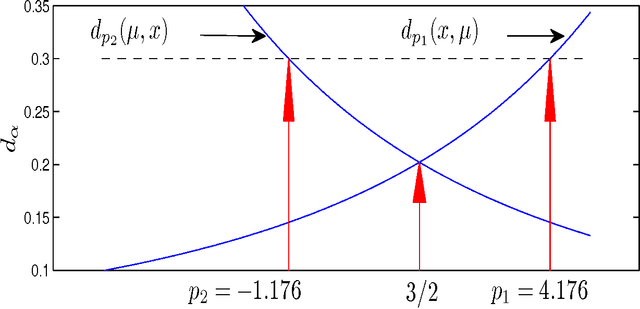
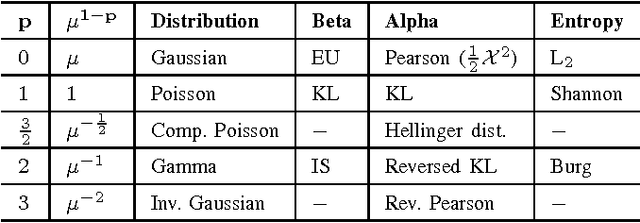
We describe the underlying probabilistic interpretation of alpha and beta divergences. We first show that beta divergences are inherently tied to Tweedie distributions, a particular type of exponential family, known as exponential dispersion models. Starting from the variance function of a Tweedie model, we outline how to get alpha and beta divergences as special cases of Csisz\'ar's $f$ and Bregman divergences. This result directly generalizes the well-known relationship between the Gaussian distribution and least squares estimation to Tweedie models and beta divergence minimization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge