AI-Driven Demodulators for Nonlinear Receivers in Shared Spectrum with High-Power Blockers
Paper and Code
Jan 24, 2022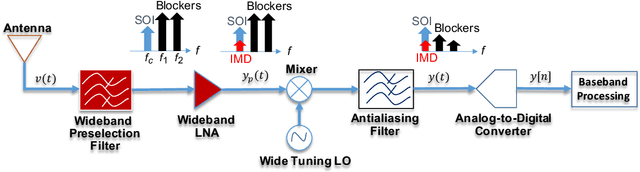

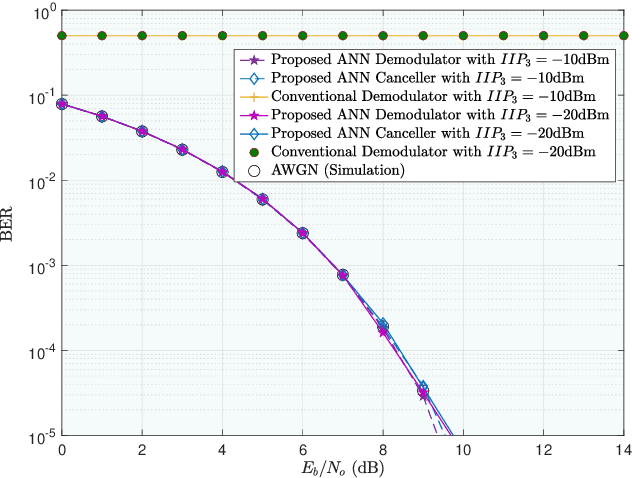

Research has shown that communications systems and receivers suffer from high power adjacent channel signals, called blockers, that drive the radio frequency (RF) front end into nonlinear operation. Since simple systems, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), will coexist with sophisticated communications transceivers, radars and other spectrum consumers, these need to be protected employing a simple, yet adaptive solution to RF nonlinearity. This paper therefore proposes a flexible data driven approach that uses a simple artificial neural network (ANN) to aid in the removal of the third order intermodulation distortion (IMD) as part of the demodulation process. We introduce and numerically evaluate two artificial intelligence (AI)-enhanced receivers-ANN as the IMD canceler and ANN as the demodulator. Our results show that a simple ANN structure can significantly improve the bit error rate (BER) performance of nonlinear receivers with strong blockers and that the ANN architecture and configuration depends mainly on the RF front end characteristics, such as the third order intercept point (IP3). We therefore recommend that receivers have hardware tags and ways to monitor those over time so that the AI and software radio processing stack can be effectively customized and automatically updated to deal with changing operating conditions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge