Affordance Extraction and Inference based on Semantic Role Labeling
Paper and Code
Sep 03, 2018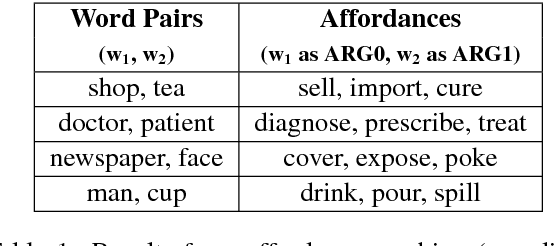
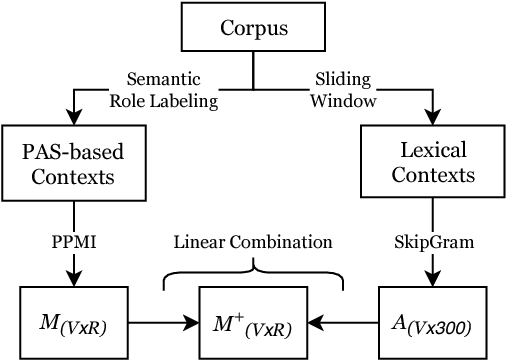
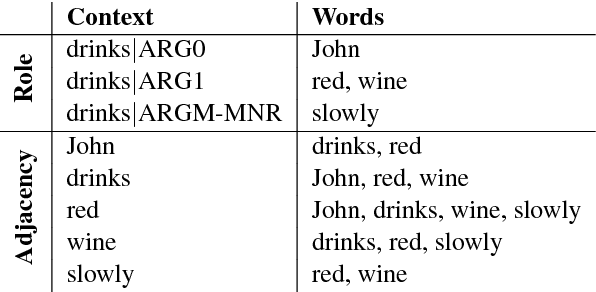
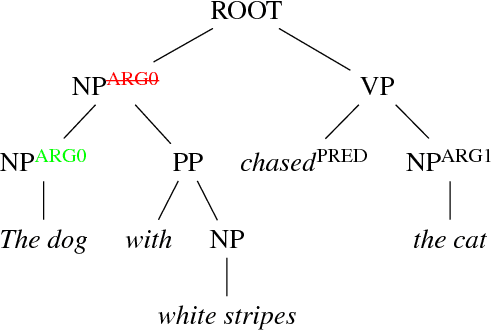
Common-sense reasoning is becoming increasingly important for the advancement of Natural Language Processing. While word embeddings have been very successful, they cannot explain which aspects of 'coffee' and 'tea' make them similar, or how they could be related to 'shop'. In this paper, we propose an explicit word representation that builds upon the Distributional Hypothesis to represent meaning from semantic roles, and allow inference of relations from their meshing, as supported by the affordance-based Indexical Hypothesis. We find that our model improves the state-of-the-art on unsupervised word similarity tasks while allowing for direct inference of new relations from the same vector space.
* Accepted at FEVER - EMNLP 2018
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge