Adversarial Vulnerability Bounds for Gaussian Process Classification
Paper and Code
Sep 19, 2019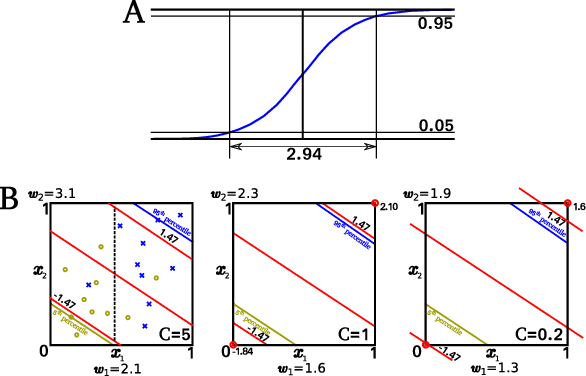

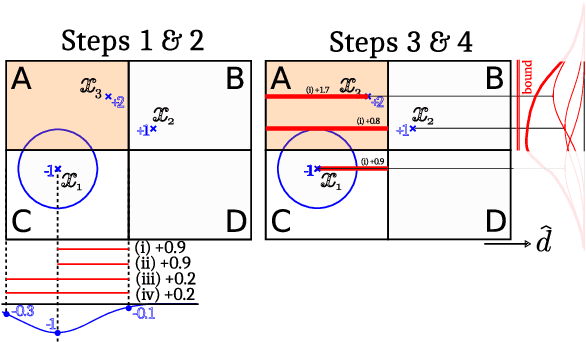

Machine learning (ML) classification is increasingly used in safety-critical systems. Protecting ML classifiers from adversarial examples is crucial. We propose that the main threat is that of an attacker perturbing a confidently classified input to produce a confident misclassification. To protect against this we devise an adversarial bound (AB) for a Gaussian process classifier, that holds for the entire input domain, bounding the potential for any future adversarial method to cause such misclassification. This is a formal guarantee of robustness, not just an empirically derived result. We investigate how to configure the classifier to maximise the bound, including the use of a sparse approximation, leading to the method producing a practical, useful and provably robust classifier, which we test using a variety of datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge