Adversarial Representation Learning for Text-to-Image Matching
Paper and Code
Aug 28, 2019
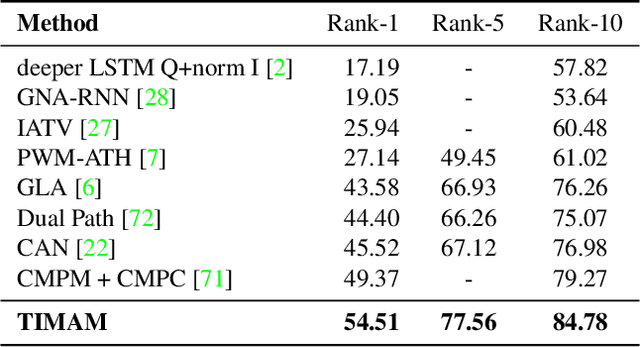

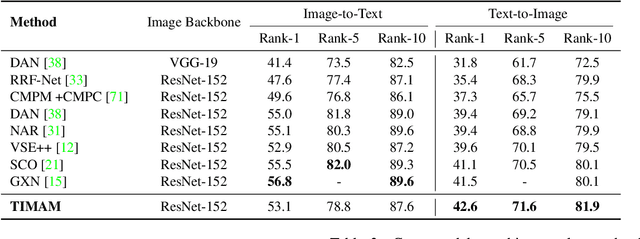
For many computer vision applications such as image captioning, visual question answering, and person search, learning discriminative feature representations at both image and text level is an essential yet challenging problem. Its challenges originate from the large word variance in the text domain as well as the difficulty of accurately measuring the distance between the features of the two modalities. Most prior work focuses on the latter challenge, by introducing loss functions that help the network learn better feature representations but fail to account for the complexity of the textual input. With that in mind, we introduce TIMAM: a Text-Image Modality Adversarial Matching approach that learns modality-invariant feature representations using adversarial and cross-modal matching objectives. In addition, we demonstrate that BERT, a publicly-available language model that extracts word embeddings, can successfully be applied in the text-to-image matching domain. The proposed approach achieves state-of-the-art cross-modal matching performance on four widely-used publicly-available datasets resulting in absolute improvements ranging from 2% to 5% in terms of rank-1 accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge