Advancing GraphSAGE with A Data-Driven Node Sampling
Paper and Code
Apr 29, 2019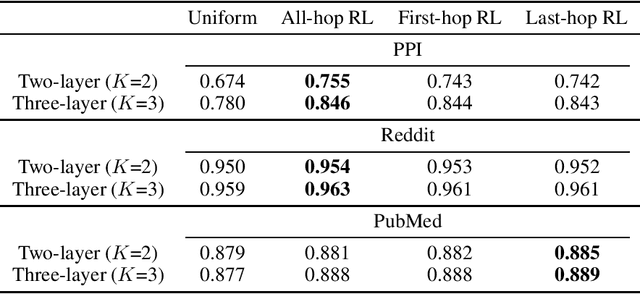
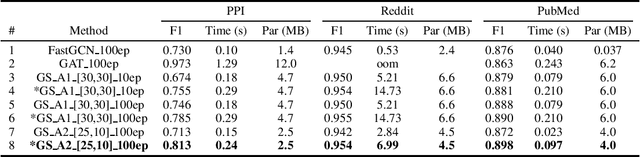
As an efficient and scalable graph neural network, GraphSAGE has enabled an inductive capability for inferring unseen nodes or graphs by aggregating subsampled local neighborhoods and by learning in a mini-batch gradient descent fashion. The neighborhood sampling used in GraphSAGE is effective in order to improve computing and memory efficiency when inferring a batch of target nodes with diverse degrees in parallel. Despite this advantage, the default uniform sampling suffers from high variance in training and inference, leading to sub-optimum accuracy. We propose a new data-driven sampling approach to reason about the real-valued importance of a neighborhood by a non-linear regressor, and to use the value as a criterion for subsampling neighborhoods. The regressor is learned using a value-based reinforcement learning. The implied importance for each combination of vertex and neighborhood is inductively extracted from the negative classification loss output of GraphSAGE. As a result, in an inductive node classification benchmark using three datasets, our method enhanced the baseline using the uniform sampling, outperforming recent variants of a graph neural network in accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge