Adopting the FAB-MAP algorithm for indoor localization with WiFi fingerprints
Paper and Code
Apr 28, 2017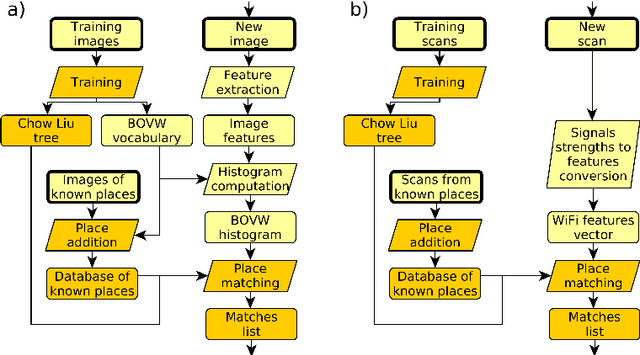
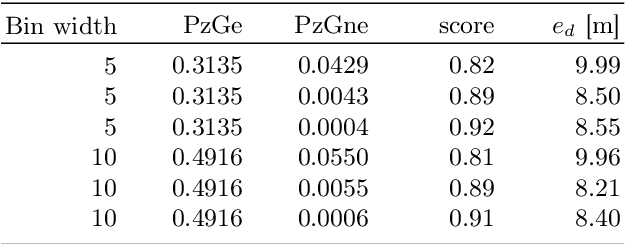
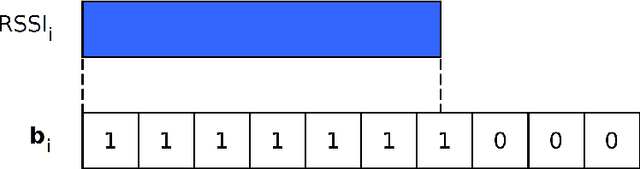

Personal indoor localization is usually accomplished by fusing information from various sensors. A common choice is to use the WiFi adapter that provides information about Access Points that can be found in the vicinity. Unfortunately, state-of-the-art approaches to WiFi-based localization often employ very dense maps of the WiFi signal distribution, and require a time-consuming process of parameter selection. On the other hand, camera images are commonly used for visual place recognition, detecting whenever the user observes a scene similar to the one already recorded in a database. Visual place recognition algorithms can work with sparse databases of recorded scenes and are in general simple to parametrize. Therefore, we propose a WiFi-based global localization method employing the structure of the well-known FAB-MAP visual place recognition algorithm. Similarly to FAB-MAP our method uses Chow-Liu trees to estimate a joint probability distribution of re-observation of a place given a set of features extracted at places visited so far. However, we are the first who apply this idea to recorded WiFi scans instead of visual words. The new method is evaluated on the UJIIndoorLoc dataset used in the EvAAL competition, allowing fair comparison with other solutions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge