Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Control of a Spherical Rolling Robot Using Sliding-Mode-Control-Theory-Based Online Learning Algorithm
Paper and Code
Apr 14, 2021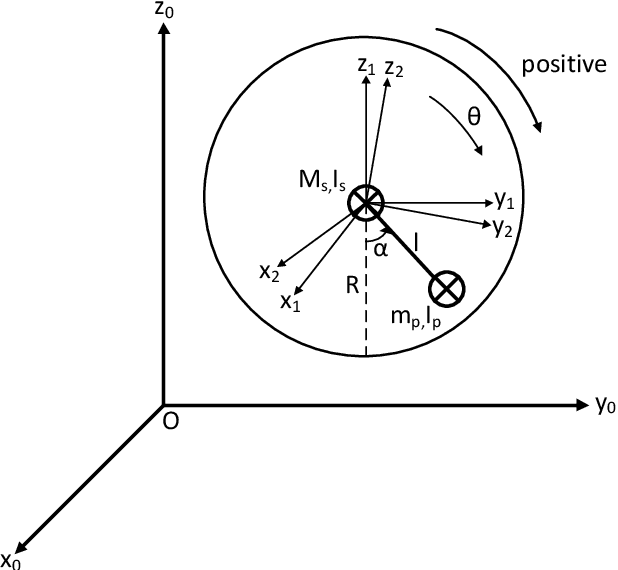
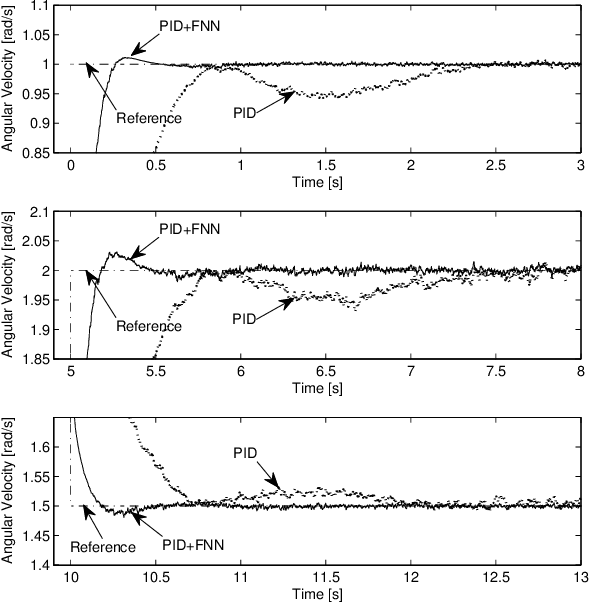
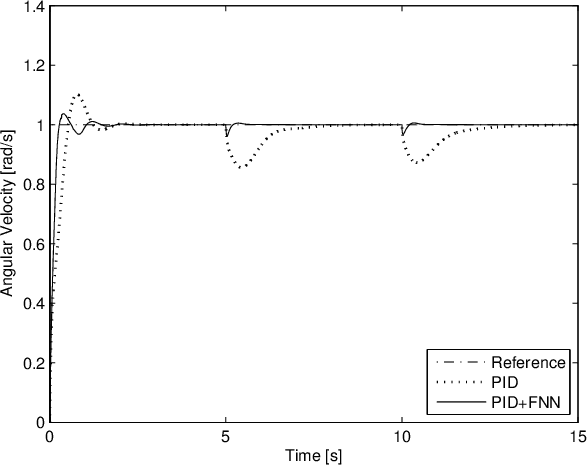
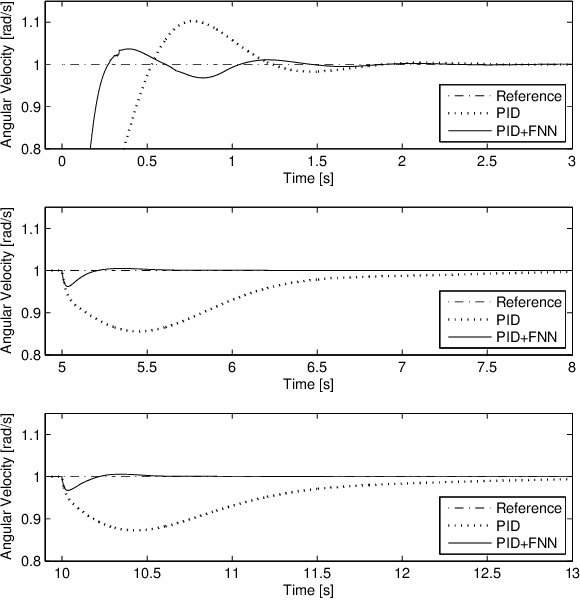
As a model is only an abstraction of the real system, unmodeled dynamics, parameter variations, and disturbances can result in poor performance of a conventional controller based on this model. In such cases, a conventional controller cannot remain well tuned. This paper presents the control of a spherical rolling robot by using an adaptive neuro-fuzzy controller in combination with a sliding-mode control (SMC)-theory-based learning algorithm. The proposed control structure consists of a neuro-fuzzy network and a conventional controller which is used to guarantee the asymptotic stability of the system in a compact space. The parameter updating rules of the neuro-fuzzy system using SMC theory are derived, and the stability of the learning is proven using a Lyapunov function. The simulation results show that the control scheme with the proposed SMC-theory-based learning algorithm is able to not only eliminate the steady-state error but also improve the transient response performance of the spherical rolling robot without knowing its dynamic equations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge