Adaptive Lasso, Transfer Lasso, and Beyond: An Asymptotic Perspective
Paper and Code
Aug 30, 2023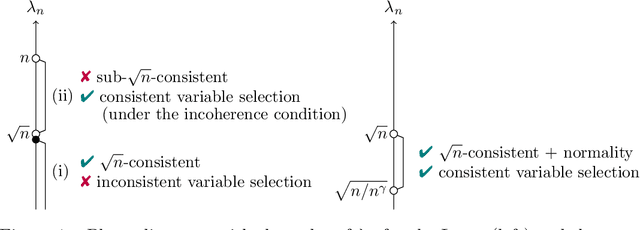

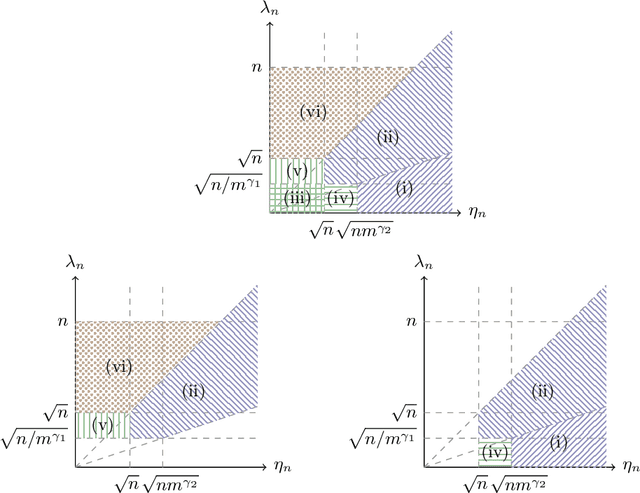
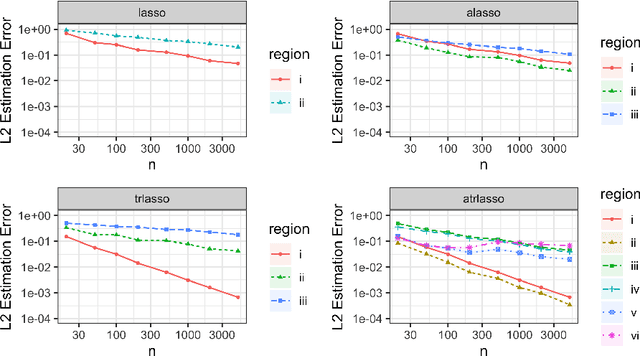
This paper presents a comprehensive exploration of the theoretical properties inherent in the Adaptive Lasso and the Transfer Lasso. The Adaptive Lasso, a well-established method, employs regularization divided by initial estimators and is characterized by asymptotic normality and variable selection consistency. In contrast, the recently proposed Transfer Lasso employs regularization subtracted by initial estimators with the demonstrated capacity to curtail non-asymptotic estimation errors. A pivotal question thus emerges: Given the distinct ways the Adaptive Lasso and the Transfer Lasso employ initial estimators, what benefits or drawbacks does this disparity confer upon each method? This paper conducts a theoretical examination of the asymptotic properties of the Transfer Lasso, thereby elucidating its differentiation from the Adaptive Lasso. Informed by the findings of this analysis, we introduce a novel method, one that amalgamates the strengths and compensates for the weaknesses of both methods. The paper concludes with validations of our theory and comparisons of the methods via simulation experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge