Adaptive Acoustic Flow-Based Navigation with 3D Sonar Sensor Fusion
Paper and Code
Aug 23, 2022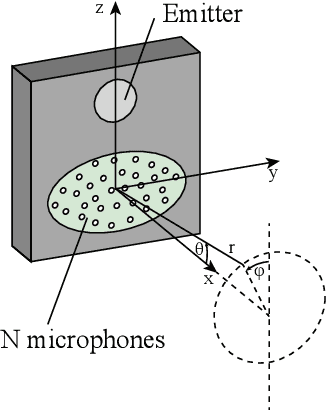
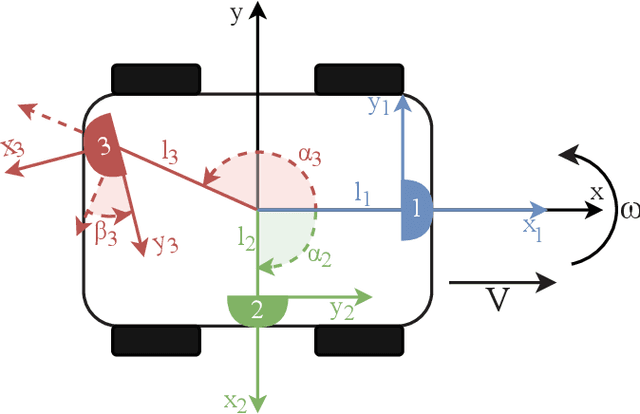
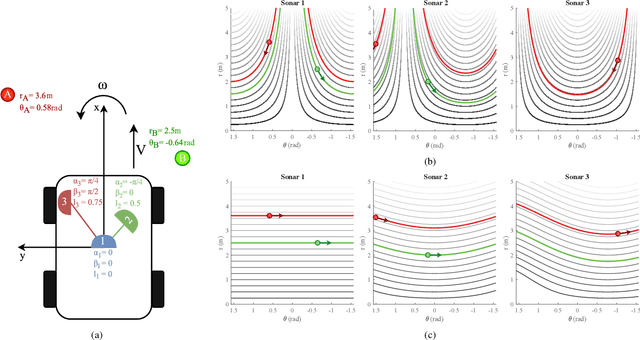
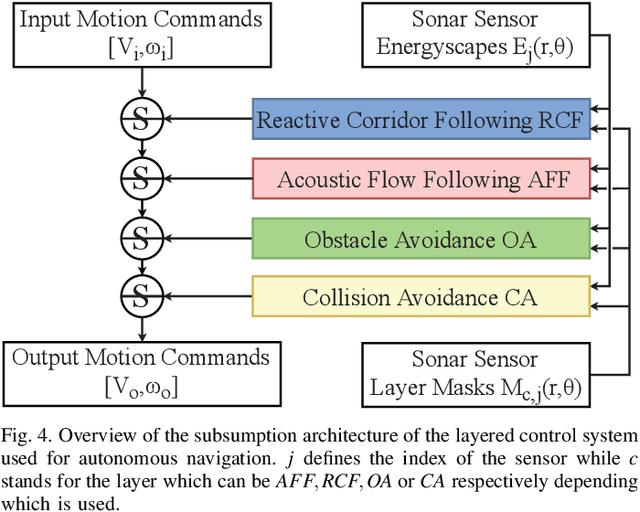
Navigating spatially varied and dynamic environments is one of the key tasks for autonomous agents. In this paper we present a novel method of navigating a mobile platform with one or multiple 3D-sonar sensors. Moving a mobile platform and subsequently any 3D-sonar sensor on it, will create signature variations over time of the echoed reflections in the sensor readings. An approach is presented to create a predictive model of these signature variations for any motion type. Furthermore, the model is adaptive and works for any position and orientation of one or multiple sonar sensors on a mobile platform. We propose to use this adaptive model and fuse all sensory readings to create a layered control system allowing a mobile platform to perform a set of primitive motions such as collision avoidance, obstacle avoidance, wall following and corridor following behaviours to navigate an environment with dynamically moving objects within it. This paper describes the underlying theoretical base of the entire navigation model and validates it in a simulated environment with results that shows the system is stable and delivers expected behaviour for several tested spatial configurations of one or multiple sonar sensors that can complete an autonomous navigation task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge