AdaPT-GMM: Powerful and robust covariate-assisted multiple testing
Paper and Code
Jun 30, 2021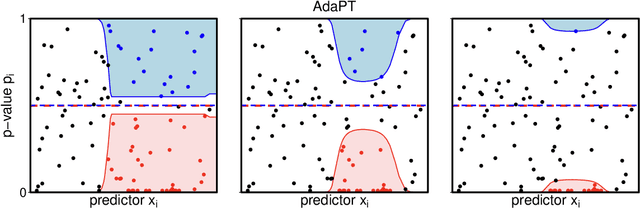
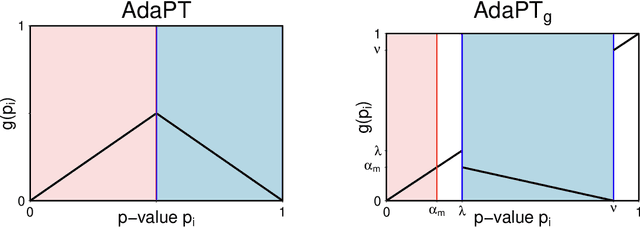
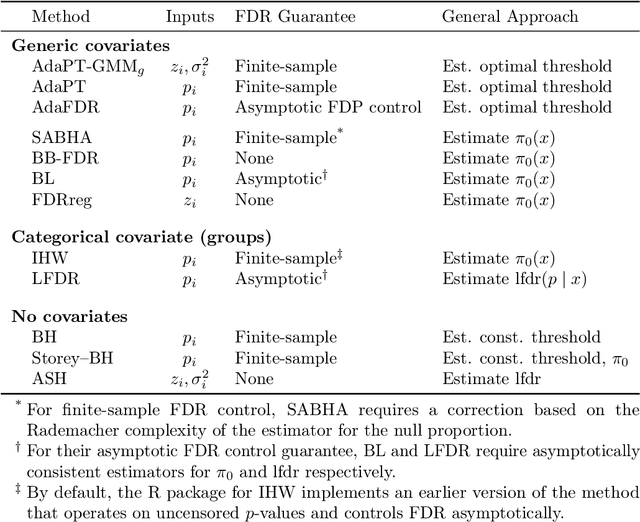
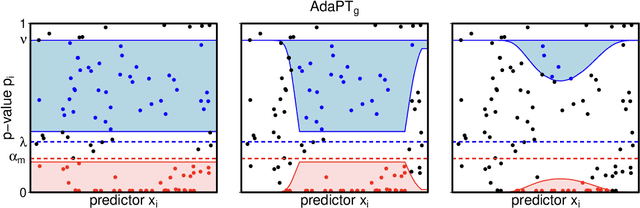
We propose a new empirical Bayes method for covariate-assisted multiple testing with false discovery rate (FDR) control, where we model the local false discovery rate for each hypothesis as a function of both its covariates and p-value. Our method refines the adaptive p-value thresholding (AdaPT) procedure by generalizing its masking scheme to reduce the bias and variance of its false discovery proportion estimator, improving the power when the rejection set is small or some null p-values concentrate near 1. We also introduce a Gaussian mixture model for the conditional distribution of the test statistics given covariates, modeling the mixing proportions with a generic user-specified classifier, which we implement using a two-layer neural network. Like AdaPT, our method provably controls the FDR in finite samples even if the classifier or the Gaussian mixture model is misspecified. We show in extensive simulations and real data examples that our new method, which we call AdaPT-GMM, consistently delivers high power relative to competing state-of-the-art methods. In particular, it performs well in scenarios where AdaPT is underpowered, and is especially well-suited for testing composite null hypothesis, such as whether the effect size exceeds a practical significance threshold.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge