Active Learning for Automated Visual Inspection of Manufactured Products
Paper and Code
Sep 06, 2021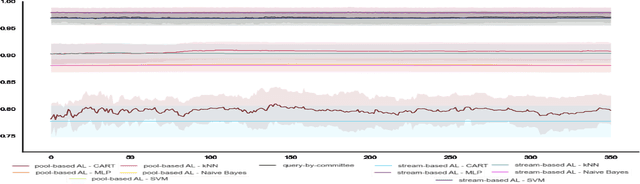
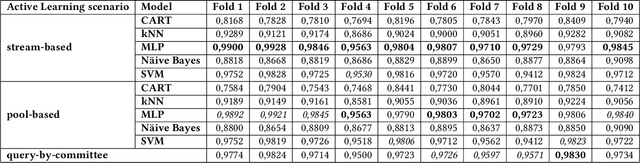

Quality control is a key activity performed by manufacturing enterprises to ensure products meet quality standards and avoid potential damage to the brand's reputation. The decreased cost of sensors and connectivity enabled an increasing digitalization of manufacturing. In addition, artificial intelligence enables higher degrees of automation, reducing overall costs and time required for defect inspection. In this research, we compare three active learning approaches and five machine learning algorithms applied to visual defect inspection with real-world data provided by Philips Consumer Lifestyle BV. Our results show that active learning reduces the data labeling effort without detriment to the models' performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge