A weakly supervised sequence tagging and grammar induction approach to semantic frame slot filling
Paper and Code
Jun 15, 2019
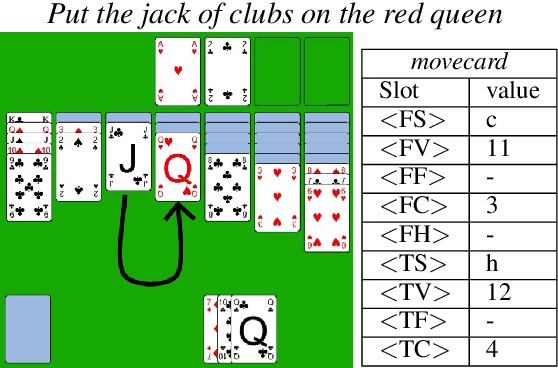
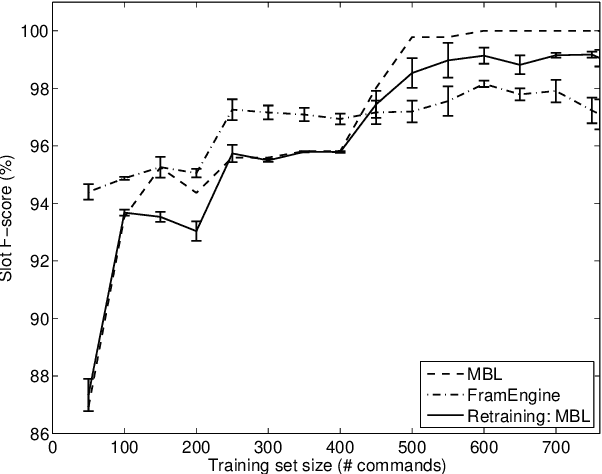
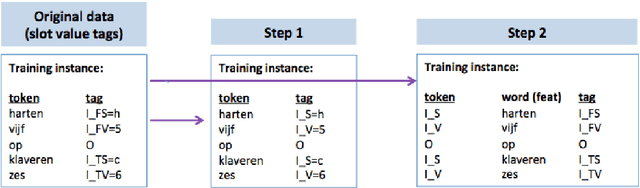
This paper describes continuing work on semantic frame slot filling for a command and control task using a weakly-supervised approach. We investigate the advantages of using retraining techniques that take the output of a hierarchical hidden markov model as input to two inductive approaches: (1) discriminative sequence labelers based on conditional random fields and memory-based learning and (2) probabilistic context-free grammar induction. Experimental results show that this setup can significantly improve F-scores without the need for additional information sources. Furthermore, qualitative analysis shows that the weakly supervised technique is able to automatically induce an easily interpretable and syntactically appropriate grammar for the domain and task at hand.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge