A Versatile Multi-Robot Monte Carlo Tree Search Planner for On-Line Coverage Path Planning
Paper and Code
Feb 11, 2020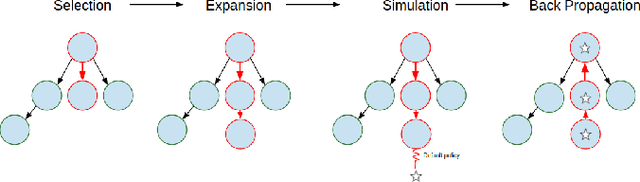
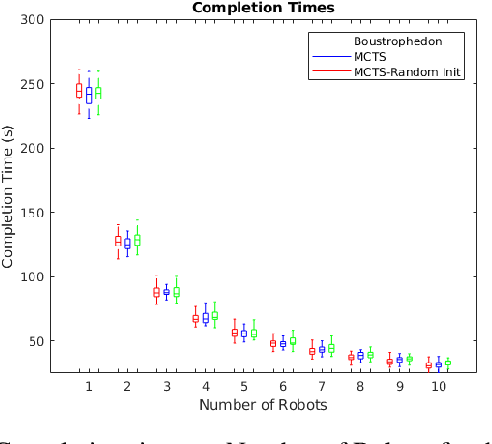
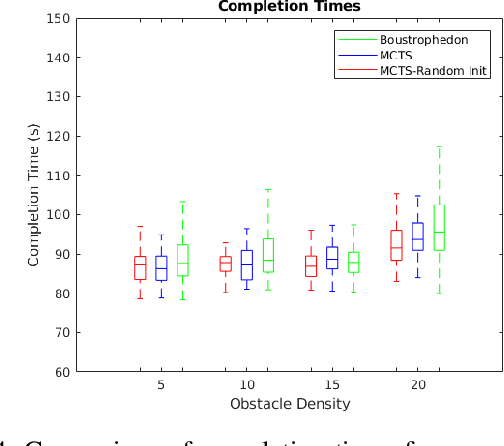
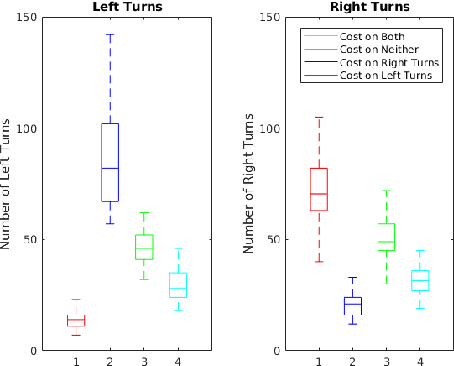
Mobile robots hold great promise in reducing the need for humans to perform jobs such as vacuuming, seeding,harvesting, painting, search and rescue, and inspection. In practice, these tasks must often be done without an exact map of the area and could be completed more quickly through the use of multiple robots working together. The task of simultaneously covering and mapping an area with multiple robots is known as multi-robot on-line coverage and is a growing area of research. Many multi-robot on-line coverage path planning algorithms have been developed as extensions of well established off-line coverage algorithms. In this work we introduce a novel approach to multi-robot on-line coverage path planning based on a method borrowed from game theory and machine learning- Monte Carlo Tree Search. We implement a Monte Carlo Tree Search planner and compare completion times against a Boustrophedon-based on-line multi-robot planner. The MCTS planner is shown to perform on par with the conventional Boustrophedon algorithm in simulations varying the number of robots and the density of obstacles in the map. The versatility of the MCTS planner is demonstrated by incorporating secondary objectives such as turn minimization while performing the same coverage task. The versatility of the MCTS planner suggests it is well suited to many multi-objective tasks that arise in mobile robotics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge