A universal synthetic dataset for machine learning on spectroscopic data
Paper and Code
Jun 14, 2022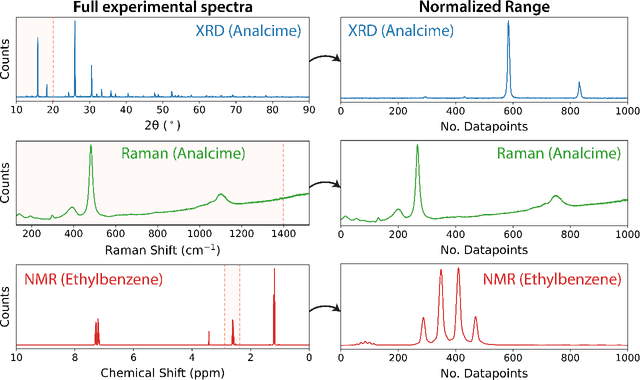
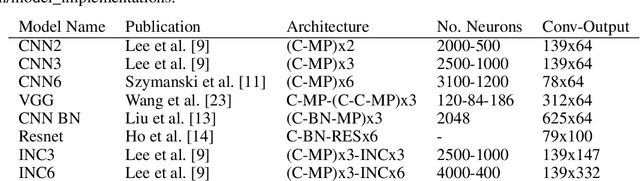
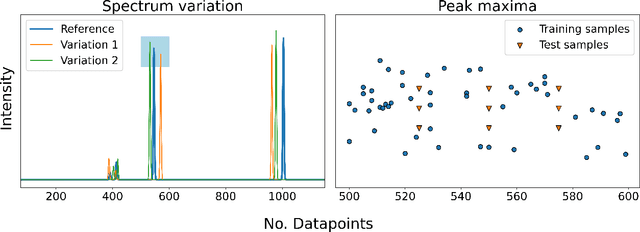
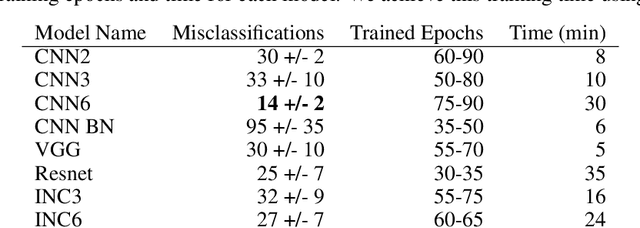
To assist in the development of machine learning methods for automated classification of spectroscopic data, we have generated a universal synthetic dataset that can be used for model validation. This dataset contains artificial spectra designed to represent experimental measurements from techniques including X-ray diffraction, nuclear magnetic resonance, and Raman spectroscopy. The dataset generation process features customizable parameters, such as scan length and peak count, which can be adjusted to fit the problem at hand. As an initial benchmark, we simulated a dataset containing 35,000 spectra based on 500 unique classes. To automate the classification of this data, eight different machine learning architectures were evaluated. From the results, we shed light on which factors are most critical to achieve optimal performance for the classification task. The scripts used to generate synthetic spectra, as well as our benchmark dataset and evaluation routines, are made publicly available to aid in the development of improved machine learning models for spectroscopic analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge