A two-stage speaker extraction algorithm under adverse acoustic conditions using a single-microphone
Paper and Code
Mar 13, 2023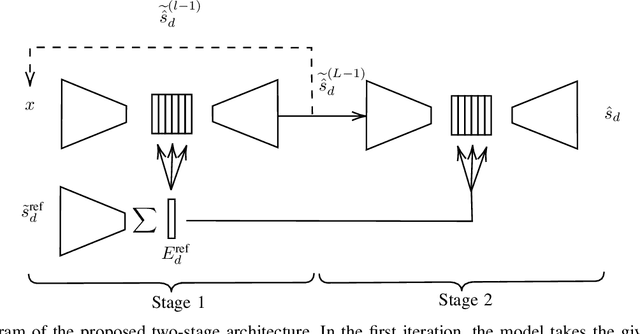
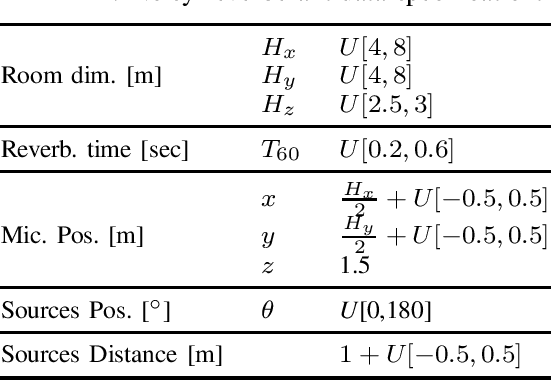
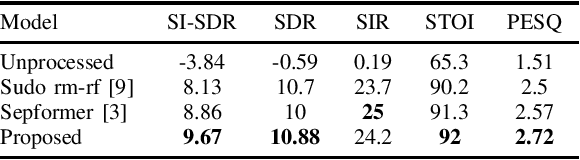
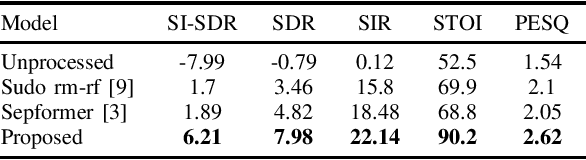
In this work, we present a two-stage method for speaker extraction under reverberant and noisy conditions. Given a reference signal of the desired speaker, the clean, but the still reverberant, desired speaker is first extracted from the noisy-mixed signal. In the second stage, the extracted signal is further enhanced by joint dereverberation and residual noise and interference reduction. The proposed architecture comprises two sub-networks, one for the extraction task and the second for the dereverberation task. We present a training strategy for this architecture and show that the performance of the proposed method is on par with other state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods when applied to the WHAMR! dataset. Furthermore, we present a new dataset with more realistic adverse acoustic conditions and show that our method outperforms the competing methods when applied to this dataset as well.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge